 | |
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Trade names | Cerazette, Lovima, Hana, others |
| Other names | DSG; ORG-2969; 3-Deketo-11-methylene-17α-ethynyl-18-methyl-19-nortestosterone; 11-Methylene-17α-ethynyl-18-methylestr-4-en-17β-ol |
| AHFS/Drugs.com | Multum Consumer Information |
| MedlinePlus | a601050 |
| License data |
|
| Routes of administration | By mouth[1] |
| Drug class | Progestogen |
| ATC code | |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status | |
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Bioavailability | 76% (range 40–100%)[11][12] |
| Protein binding | Desogestrel: 99%:[13] • Albumin: 99% Etonogestrel: 95–98%:[1][14] • Albumin: 65–66% • SHBG: 30–32% • Free: 2–5% |
| Metabolism | Liver, intestines (5α- and 5β-reductase, cytochrome P450 enzymes, others)[14] |
| Metabolites | • Etonogestrel[14][1][11] • Others[13][14][11] |
| Elimination half-life | Desogestrel: 1.5 hours[13] Etonogestrel: 21–38 hrs[13][15] |
| Excretion | Urine: 50%[13] Feces: 35%[13] |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| IUPHAR/BPS | |
| DrugBank | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.053.555 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
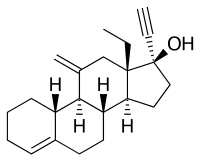
| Formula | C22H30O |
| Molar mass | 310.481 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| Melting point | 109 to 110 °C (228 to 230 °F) |
| |
| |
| (verify) | |
Desogestrel is a progestin medication which is used in birth control pills.[1][14] It is also used in the treatment of menopausal symptoms in women.[1] The medication is available and used alone or in combination with an estrogen.[1][14] It is taken by mouth.[1]
Side effects of desogestrel include menstrual irregularities, headaches, nausea, breast tenderness, mood changes, acne, increased hair growth, and others.[1] Desogestrel is a progestin, or a synthetic progestogen, and hence is an agonist of the progesterone receptor, the biological target of progestogens like progesterone.[1][14] It has very weak androgenic and glucocorticoid activity and no other important hormonal activity.[14] The medication is a prodrug of etonogestrel (3-ketodesogestrel) in the body.[1][14]
Desogestrel was discovered in 1972 and was introduced for medical use in Europe in 1981.[16][13][17] It became available in the United States in 1992.[18][19][20] Desogestrel is sometimes referred to as a "third-generation" progestin.[21] Likenorethisterone and Norgestrel, Desogestrel is widely available as a progestogen-only "mini pill" for birth control.[22][23][24] Desogestrel is marketed widely throughout the world.[25] It is available as a generic medication.[26] In 2020, the version with ethinylestradiol was the 120th most commonly prescribed medication in the United States, with more than 5 million prescriptions.[27][28]
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j Stone SC (December 1995). "Desogestrel". Clinical Obstetrics and Gynecology. 38 (4): 821–828. doi:10.1097/00003081-199538040-00017. PMID 8616978.
- ^ "Marvelon Tablets - Summary of Product Characteristics (SmPC)". (emc). 11 March 2021. Archived from the original on 10 July 2021. Retrieved 9 July 2021.
- ^ "Mercilon Tablets - Summary of Product Characteristics (SmPC)". (emc). 11 March 2021. Archived from the original on 10 July 2021. Retrieved 9 July 2021.
- ^ "Cerazette 75 microgram film-coated tablet - Summary of Product Characteristics (SmPC)". (emc). 20 November 2020. Archived from the original on 10 July 2021. Retrieved 9 July 2021.
- ^ Cite error: The named reference
Hana SmPCwas invoked but never defined (see the help page). - ^ "Lovima 75 microgram film-coated tablets - Summary of Product Characteristics (SmPC)". (emc). 9 July 2021. Archived from the original on 6 July 2022. Retrieved 6 July 2022.
- ^ "Apri 28 Day- desogestrel and ethinyl estradiol kit". DailyMed. Archived from the original on 10 July 2021. Retrieved 9 July 2021.
- ^ "Mircette- desogestrel/ethinyl estradiol and ethinyl estradiol kit". DailyMed. Archived from the original on 10 July 2021. Retrieved 9 July 2021.
- ^ "Kariva- desogestrel/ethinyl estradiol and ethinyl estradiol kit". DailyMed. Archived from the original on 10 July 2021. Retrieved 9 July 2021.
- ^ "Velivet Triphasic Regimen- desogestrel and ethinyl estradiol kit". DailyMed. Archived from the original on 10 July 2021. Retrieved 9 July 2021.
- ^ a b c Cite error: The named reference
pmid8447355was invoked but never defined (see the help page). - ^ Fotherby K (August 1996). "Bioavailability of orally administered sex steroids used in oral contraception and hormone replacement therapy". Contraception. 54 (2): 59–69. doi:10.1016/0010-7824(96)00136-9. PMID 8842581.
- ^ a b c d e f g Cite error: The named reference
RunnebaumRabe2012was invoked but never defined (see the help page). - ^ a b c d e f g h i Kuhl H (February 1996). "Comparative pharmacology of newer progestogens". Drugs. 51 (2): 188–215. doi:10.2165/00003495-199651020-00002. PMID 8808163. S2CID 1019532.
- ^ Cite error: The named reference
Mosby2001was invoked but never defined (see the help page). - ^ Cite error: The named reference
Kuhl2011was invoked but never defined (see the help page). - ^ Cite error: The named reference
Holtsclaw2007was invoked but never defined (see the help page). - ^ Cite error: The named reference
pmid8520092was invoked but never defined (see the help page). - ^ Cite error: The named reference
KornsteinClayton2004was invoked but never defined (see the help page). - ^ Cite error: The named reference
pmid8178905was invoked but never defined (see the help page). - ^ Carp HJ (9 April 2015). Progestogens in Obstetrics and Gynecology. Springer. pp. 112, 136. ISBN 978-3-319-14385-9.
- ^ Grimes DA, Lopez LM, O'Brien PA, Raymond EG (November 2013). "Progestin-only pills for contraception". The Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews (11): CD007541. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD007541.pub3. PMID 24226383.
- ^ Hussain SF (February 2004). "Progestogen-only pills and high blood pressure: is there an association? A literature review". Contraception. 69 (2): 89–97. doi:10.1016/j.contraception.2003.09.002. PMID 14759612.
- ^ "Opill: Package Insert / Prescribing Information". Drugs.com. Retrieved 30 September 2024.
- ^ Cite error: The named reference
Drugs.comwas invoked but never defined (see the help page). - ^ "Generic Desogen Availability". Archived from the original on 6 January 2018. Retrieved 6 January 2018.
- ^ "The Top 300 of 2020". ClinCalc. Retrieved 7 October 2022.
- ^ "Desogestrel; Ethinyl Estradiol - Drug Usage Statistics". ClinCalc. Retrieved 7 October 2022.