| |||
| Names | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
Dichloroacetic acid | |||
| Other names
Dichloroethanoic acid, bichloroacetic acid, DCA, BCA, dichloracetic acid, bichloracetic acid
| |||
| Identifiers | |||
3D model (JSmol)
|
|||
| 1098596 | |||
| ChEBI | |||
| ChEMBL | |||
| ChemSpider | |||
| DrugBank | |||
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.001.098 | ||
| EC Number |
| ||
| 2477 | |||
| KEGG | |||
| MeSH | Dichloroacetate | ||
PubChem CID
|
|||
| RTECS number |
| ||
| UNII | |||
| UN number | 1764 | ||
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|||
| |||
| |||
| Properties | |||
| C2H2Cl2O2 | |||
| Molar mass | 128.94 g·mol−1 | ||
| Appearance | Colorless liquid | ||
| Density | 1.5634 g/cm3 (20 °C) | ||
| Melting point | 9 to 11 °C (48 to 52 °F; 282 to 284 K) | ||
| Boiling point | 194 °C (381 °F; 467 K) | ||
| miscible | |||
| Solubility | miscible with ethanol, diethyl ether[1] | ||
| Acidity (pKa) | 1.35[1] | ||
| -58.2·10−6 cm3/mol | |||
| Thermochemistry | |||
Std enthalpy of
formation (ΔfH⦵298) |
−496.3 kJ·mol−1[1] | ||
| Hazards | |||
| GHS labelling: | |||
 
| |||
| Warning | |||
| H314, H400 | |||
| P260, P264, P273, P280, P301+P330+P331, P303+P361+P353, P304+P340, P305+P351+P338, P310, P321, P363, P391, P405, P501 | |||
| NFPA 704 (fire diamond) | |||
| Safety data sheet (SDS) | MSDS (jtbaker) | ||
| Related compounds | |||
Related chloroacetic acids
|
Chloroacetic acid Trichloroacetic acid | ||
Related compounds
|
Acetic acid Difluoroacetic acid Dibromoacetic acid | ||
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |||
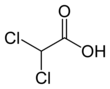
Dichloroacetic acid (DCA), sometimes called bichloroacetic acid (BCA), is the organic compound with formula CHCl2CO2H. It is an analogue of acetic acid, in which 2 of the 3 hydrogen atoms of the methyl group have been replaced by chlorine atoms. Like the other chloroacetic acids, it has various practical applications. The salts and esters of dichloroacetic acid are called dichloroacetates.