| Dictyostelium | |
|---|---|
| |
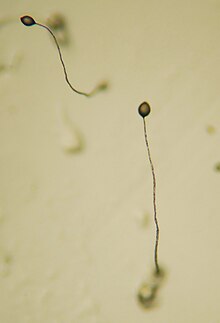
| Dictyostelium fruiting bodies | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Domain: | Eukaryota |
| Phylum: | Amoebozoa |
| Class: | Dictyostelia |
| Order: | Dictyosteliida |
| Family: | Dictyosteliidae |
| Genus: | Dictyostelium Bref. |
| Type species | |
| Dictyostelium mucoroides Brefeld 1869
| |
| Synonyms | |
| |




Dictyostelium is a genus of single- and multi-celled eukaryotic, phagotrophic bacterivores. Though they are Protista and in no way fungal, they traditionally are known as "slime molds". They are present in most terrestrial ecosystems as a normal and often abundant component of the soil microflora, and play an important role in the maintenance of balanced bacterial populations in soils.[1][2]
The genus Dictyostelium is in the order Dictyosteliida, the so-called cellular slime molds or social amoebae. In turn the order is in the infraphylum Mycetozoa. Members of the order are Protista of great theoretical interest in biology because they have aspects of both unicellularity and multicellularity. The individual cells in their independent phase are common on organic detritus or in damp soils and caves. In this phase they are amoebae. Typically, the amoebal cells grow separately and wander independently, feeding mainly on bacteria. However, they interact to form multi-cellular structures following starvation. Groups of up to about 100,000 cells signal each other by releasing chemoattractants such as cyclic AMP (cAMP) or glorin. They then coalesce by chemotaxis to form an aggregate that becomes surrounded by an extracellular matrix. The aggregate forms a fruiting body, with cells differentiating individually into different components of the final structure.[3] In some species, the whole aggregate may move collectively – forming a structure known as a grex or "slug" – before finally forming a fruiting body. Basic processes of development such as differential cell sorting, pattern formation, stimulus-induced gene expression, and cell-type regulation are common to Dictyostelium and metazoans. For further detail see family Dictyostelid.
- ^ Landolt, C. (2006). "Dictyostelid Cellular Slime Molds from Caves" (PDF). Journal of Cave and Karst Studies. 68 (1): 22–26.
- ^ Pears, Catherine J.; Gross, Julian D. (2021-03-01). "Microbe Profile: Dictyostelium discoideum: model system for development, chemotaxis and biomedical research". Microbiology. 167 (3). doi:10.1099/mic.0.001040. ISSN 1350-0872. PMID 33646931. S2CID 232092012.
- ^ "About Dictyostelium". dictybase.org.