 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Trade names | Byclomine, Bentyl, Dibent, others |
| AHFS/Drugs.com | Monograph |
| MedlinePlus | a684007 |
| License data |
|
| Pregnancy category |
|
| ATC code | |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status | |
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Protein binding | >99% |
| Elimination half-life | 5 h |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| IUPHAR/BPS | |
| DrugBank | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.000.919 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
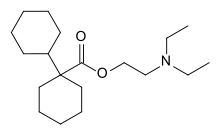
| Formula | C19H35NO2 |
| Molar mass | 309.494 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
| (verify) | |
Dicycloverine, also known as dicyclomine, sold under the brand name Bentyl among others, is a medication that is used to treat spasms of the intestines such as those that occur in irritable bowel syndrome.[1][2] It is taken by mouth or by injection into a muscle.[2] While it has been used in baby colic and enterocolitis, evidence does not support these uses.[2]
Common side effects include dry mouth, blurry vision, weakness, sleepiness, and lightheadedness.[2] Serious side effects may include psychosis and breathing problems in babies.[2] Use in pregnancy appears to be safe while use during breastfeeding is not recommended.[3] How it works is not entirely clear.[2]
Dicycloverine was approved for medical use in the United States in 1950.[2] It is available as a generic medication.[1] In 2022, it was the 176th most commonly prescribed medication in the United States, with more than 2 million prescriptions.[4][5]
- ^ a b British national formulary : BNF 76 (76 ed.). Pharmaceutical Press. 2018. p. 759. ISBN 9780857113382.
- ^ a b c d e f g "Dicyclomine Hydrochloride Monograph for Professionals". Drugs.com. American Society of Health-System Pharmacists. Retrieved 3 March 2019.
- ^ "Dicyclomine Pregnancy and Breastfeeding Warnings". Drugs.com. Retrieved 3 March 2019.
- ^ "The Top 300 of 2022". ClinCalc. Archived from the original on 30 August 2024. Retrieved 30 August 2024.
- ^ "Dicyclomine Drug Usage Statistics, United States, 2013 - 2022". ClinCalc. Retrieved 30 August 2024.