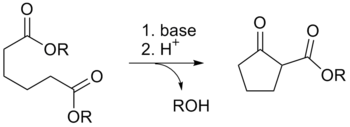| Dieckmann condensation | |
|---|---|
| Named after | Walter Dieckmann |
| Reaction type | Ring forming reaction |
| Identifiers | |
| Organic Chemistry Portal | dieckmann-condensation |
| RSC ontology ID | RXNO:0000065 |
The Dieckmann condensation is the intramolecular chemical reaction of diesters with base to give β-keto esters.[1] It is named after the German chemist Walter Dieckmann (1869–1925).[2][3] The equivalent intermolecular reaction is the Claisen condensation. Dieckmann condensations are highly effective routes to 5-, 6-, and 7-member rings, but poor for larger rings.[4]
- ^ Davis, B. R.; Garrett, P. J. Compr. Org. Synth. 1991, 2, 806-829. (Review)
- ^ Kwart, Harold; King, Kenneth (1969). "Rearrangement and cyclization reactions of carboxylic acids and esters". In S. Patai (ed.). PATAI'S Chemistry of Functional Groups: Carboxylic Acids and Esters (1969). pp. 341–373. doi:10.1002/9780470771099.ch8. ISBN 9780470771099.
- ^ Schaefer, J. P.; Bloomfield, J. J. (1967). "The Dieckmann Condensation (Including the Thorpe-Ziegler Condensation)". Organic Reactions. 15: 1–203. doi:10.1002/0471264180.or015.01. ISBN 0471264180.
- ^ Smith, Michael B.; March, Jerry (2007), Advanced Organic Chemistry: Reactions, Mechanisms, and Structure (6th ed.), New York: Wiley-Interscience, p. 1453, ISBN 978-0-471-72091-1