 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Trade names | Ortho Dienestrol, Dienoestrol, Dienoestrol Ortho, Sexadien, Cycladiene, Denestrolin, Dienol, Dinovex, Follormon, Oestrodiene, Synestrol |
| Other names | Dienoestrol; p-[(E,E)-1-Ethylidene-2-(p-hydroxyphenyl)-2-butenyl]phenol; 3,4-Di(para-hydroxyphenyl)-2,4-hexadiene |
| AHFS/Drugs.com | Micromedex Detailed Consumer Information |
| Drug class | Nonsteroidal estrogen |
| ATC code | |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| IUPHAR/BPS | |
| DrugBank | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.001.381 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
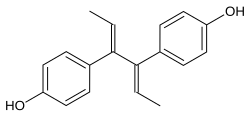
| Formula | C18H18O2 |
| Molar mass | 266.340 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
| | |
Dienestrol (INN, USAN) (brand names Dienoestrol, Denestrolin, Dienol and many others[a]), also known as dienoestrol (BAN), is a synthetic nonsteroidal estrogen medication of the stilbestrol group which is or was used to treat menopausal symptoms in the United States and Europe.[1][2][3][4] It has been studied for use by rectal administration in the treatment of prostate cancer in men as well.[5] The medication was introduced in the U.S. in 1947 by Schering as Synestrol and in France in 1948 as Cycladiene.[4] Dienestrol is a close analogue of diethylstilbestrol.[6] It has approximately 223% and 404% of the affinity of estradiol at the ERα and ERβ, respectively.[7]
Dienestrol diacetate (brand names Faragynol, Gynocyrol, others) also exists and has been used medically.[2]
Cite error: There are <ref group=lower-alpha> tags or {{efn}} templates on this page, but the references will not show without a {{reflist|group=lower-alpha}} template or {{notelist}} template (see the help page).
- ^ Index Nominum 2000: International Drug Directory. Taylor & Francis. January 2000. pp. 331–. ISBN 978-3-88763-075-1.
- ^ a b J. Elks (14 November 2014). The Dictionary of Drugs: Chemical Data: Chemical Data, Structures and Bibliographies. Springer. pp. 390–. ISBN 978-1-4757-2085-3.
- ^ Muller (19 June 1998). European Drug Index: European Drug Registrations, Fourth Edition. CRC Press. pp. 361–. ISBN 978-3-7692-2114-5.
- ^ a b William Andrew Publishing (22 October 2013). Pharmaceutical Manufacturing Encyclopedia, 3rd Edition. Elsevier. pp. 1286–. ISBN 978-0-8155-1856-3.
- ^ Sambuelli M (1953). "Somministrazione degli estrogeni per via rettale nel carcinoma prostatico" [Rectal administration of estrogens in prostate carcinoma]. Minerva Urol (in Italian). 5 (1): 28–32. ISSN 0026-4989. PMID 13063334.
- ^ VITAMINS AND HORMONES. Academic Press. 1 January 1945. pp. 233–. ISBN 978-0-08-086600-0.
- ^ Kuiper GG, Carlsson B, Grandien K, Enmark E, Häggblad J, Nilsson S, Gustafsson JA (1997). "Comparison of the ligand binding specificity and transcript tissue distribution of estrogen receptors alpha and beta". Endocrinology. 138 (3): 863–70. doi:10.1210/endo.138.3.4979. PMID 9048584.