| |||
| |||
| Names | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Systematic IUPAC name
Difluorophosphate[1] | |||
| Identifiers | |||
3D model (JSmol)
|
|||
| ChemSpider | |||
PubChem CID
|
|||
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|||
| |||
| |||
| Properties | |||
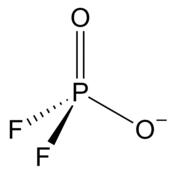
| PO2F−2 | |||
| Molar mass | 100.97 g mol−1 | ||
| Structure | |||
| Tetracoordinated at phosphorus atom | |||
| Tetrahedral at phosphorus atom | |||
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |||
Difluorophosphate or difluorodioxophosphate or phosphorodifluoridate is an anion with formula PO2F−2. It has a single negative charge and resembles perchlorate (ClO−4) and monofluorosulfonate (SO3F−) in shape and compounds.[2] These ions are isoelectronic, along with tetrafluoroaluminate, phosphate, orthosilicate, and sulfate.[2][3] It forms a series of compounds. The ion is toxic to mammals as it causes blockage to iodine uptake in the thyroid. However it is degraded in the body over several hours.[2]
Compounds containing difluorophosphate may have it as a simple uninegative ion, it may function as a difluorophosphato ligand where it is covalently bound to one or two metal atoms, or go on to form a networked solid.[4] It may be covalently bound to a non metal or an organic moiety to make an ester or an amide.
- ^ Toy, Arthur D. F. (22 Oct 2013). The Chemistry of Phosphorus. Pergamon Texts in Inorganic Chemistry. Vol. 3. Pergamon Press. pp. 536–537. ISBN 9781483147413. Retrieved 19 June 2015.
- ^ a b c Cite error: The named reference
an59was invoked but never defined (see the help page). - ^ Cite error: The named reference
Lange29was invoked but never defined (see the help page). - ^ Schulz, Christoph; Eiden, Philipp; Klose, Petra; Ermantraut, Andreas; Schmidt, Michael; Garsuch, Arnd; Krossing, Ingo (2015). "Homoleptic borates and aluminates containing the difluorophosphato ligand – [M(O2PF2)x]y− – synthesis and characterization". Dalton Trans. 44 (15): 7048–7057. doi:10.1039/c5dt00469a. PMID 25785817.

