 | |
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| AHFS/Drugs.com | International Drug Names |
| Routes of administration | By mouth |
| ATC code | |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status |
|
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Bioavailability | 12% |
| Metabolism | Liver |
| Elimination half-life | About 4–11 hours |
| Excretion | Mainly bile |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| ChEMBL | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.128.242 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
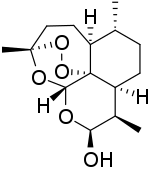
| Formula | C15H24O5 |
| Molar mass | 284.352 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
| | |
Dihydroartemisinin (also known as dihydroqinghaosu, artenimol or DHA) is a drug used to treat malaria. Dihydroartemisinin is the active metabolite of all artemisinin compounds (artemisinin, artesunate, artemether, etc.) and is also available as a drug in itself. It is a semi-synthetic derivative of artemisinin and is widely used as an intermediate in the preparation of other artemisinin-derived antimalarial drugs.[1] It is sold commercially in combination with piperaquine and has been shown to be equivalent to artemether/lumefantrine.[2]
- ^ Woo SH, Parker MH, Ploypradith P, Northrop J, Posner GH (1998). "Direct conversion of pyranose anomeric OH→F→R in the artemisinin family of antimalarial trioxanes". Tetrahedron Letters. 39 (12): 1533–6. doi:10.1016/S0040-4039(98)00132-4.
- ^ Arinaitwe E, Sandison TG, Wanzira H, Kakuru A, Homsy J, Kalamya J, et al. (December 2009). "Artemether-lumefantrine versus dihydroartemisinin-piperaquine for falciparum malaria: a longitudinal, randomized trial in young Ugandan children". Clinical Infectious Diseases. 49 (11): 1629–1637. doi:10.1086/647946. PMID 19877969.