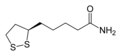
Dihydrolipoamide dehydrogenase (DLD), also known as dihydrolipoyl dehydrogenase, mitochondrial, is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the DLD gene.[5][6][7][8] DLD is a flavoprotein enzyme that oxidizes dihydrolipoamide to lipoamide.
Dihydrolipoamide dehydrogenase (DLD) is a mitochondrial enzyme that plays a vital role in energy metabolism in eukaryotes. This enzyme is required for the complete reaction of at least five different multi-enzyme complexes.[9] Additionally, DLD is a flavoenzyme oxidoreductase that contains a reactive disulfide bridge and a FAD cofactor that are directly involved in catalysis. The enzyme associates into tightly bound homodimers required for its enzymatic activity.[10]
- ^ a b c GRCh38: Ensembl release 89: ENSG00000091140 – Ensembl, May 2017
- ^ a b c GRCm38: Ensembl release 89: ENSMUSG00000020664 – Ensembl, May 2017
- ^ "Human PubMed Reference:". National Center for Biotechnology Information, U.S. National Library of Medicine.
- ^ "Mouse PubMed Reference:". National Center for Biotechnology Information, U.S. National Library of Medicine.
- ^ "Entrez Gene: dihydrolipoamide dehydrogenase".
- ^ Otulakowski G, Robinson BH (December 1987). "Isolation and sequence determination of cDNA clones for porcine and human lipoamide dehydrogenase. Homology to other disulfide oxidoreductases". The Journal of Biological Chemistry. 262 (36): 17313–8. doi:10.1016/S0021-9258(18)45379-3. PMID 3693355.
- ^ Pons G, Raefsky-Estrin C, Carothers DJ, Pepin RA, Javed AA, Jesse BW, et al. (March 1988). "Cloning and cDNA sequence of the dihydrolipoamide dehydrogenase component human alpha-ketoacid dehydrogenase complexes". Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America. 85 (5): 1422–6. Bibcode:1988PNAS...85.1422P. doi:10.1073/pnas.85.5.1422. PMC 279783. PMID 3278312.
- ^ Scherer SW, Otulakowski G, Robinson BH, Tsui LC (1991). "Localization of the human dihydrolipoamide dehydrogenase gene (DLD) to 7q31----q32". Cytogenetics and Cell Genetics. 56 (3–4): 176–7. doi:10.1159/000133081. hdl:10722/42531. PMID 2055113.
- ^ Babady NE, Pang YP, Elpeleg O, Isaya G (April 2007). "Cryptic proteolytic activity of dihydrolipoamide dehydrogenase". Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America. 104 (15): 6158–63. Bibcode:2007PNAS..104.6158B. doi:10.1073/pnas.0610618104. PMC 1851069. PMID 17404228.
- ^ Ciszak EM, Makal A, Hong YS, Vettaikkorumakankauv AK, Korotchkina LG, Patel MS (January 2006). "How dihydrolipoamide dehydrogenase-binding protein binds dihydrolipoamide dehydrogenase in the human pyruvate dehydrogenase complex". The Journal of Biological Chemistry. 281 (1): 648–55. doi:10.1074/jbc.M507850200. PMID 16263718.