| |

| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
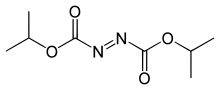
| IUPAC name
Diisopropyl azodicarboxylate
| |
| Systematic IUPAC name
Propan-2-yl (NE)-N-propan-2-yloxycarbonyliminocarbamate[1] | |
| Other names
DIAD
| |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.017.730 |
| EC Number |
|
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C8H14N2O4 | |
| Molar mass | 202.210 g·mol−1 |
| Appearance | Orange liquid |
| Density | 1.027 g/cm3 |
| Melting point | 3 to 5 °C (37 to 41 °F; 276 to 278 K) |
| Boiling point | 75 °C (167 °F; 348 K) at 0.25 mmHg |
| insoluble | |
Refractive index (nD)
|
1.418-1.422 |
| Hazards | |
| GHS labelling: | |
  
| |
| Warning | |
| H315, H319, H335, H373, H411 | |
| P260, P261, P264, P271, P273, P280, P302+P352, P304+P340, P305+P351+P338, P312, P314, P321, P332+P313, P337+P313, P362, P391, P403+P233, P405, P501 | |
| Flash point | 106 °C (223 °F; 379 K) |
| Safety data sheet (SDS) | Sigma-Aldrich |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
Diisopropyl azodicarboxylate (DIAD) is the diisopropyl ester of azodicarboxylic acid. It is used as a reagent in the production of many organic compounds. It is often used with triphenylphosphine in the Mitsunobu reaction,[2] wherein it serves as a hydride acceptor. It has also been used to generate aza-Baylis-Hillman adducts with acrylates.[3] It can also serve as a selective deprotectant of N-benzyl groups in the presence of other protecting groups.[4]
It is sometimes preferred to diethyl azodicarboxylate (DEAD) because it is more hindered, and thus less likely to form hydrazide byproducts.
One notable use of this compound is in the synthesis of Bifenazate (Floramite®).[citation needed]
- ^ https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/compound/5363146#section=IUPAC-Name&fullscreen=true
- ^ "luka DIAD on Sigma-Aldrich". Archived from the original on 2008-04-24. Retrieved 2008-11-18.
- ^ Shi, Min; Zhao, Gui-Ling (2004). "Aza-Baylis–Hillman reactions of diisopropyl azodicarboxylate or diethyl azodicarboxylate with acrylates and acrylonitrile". Tetrahedron. 60 (9): 2083–2089. doi:10.1016/j.tet.2003.12.059.
- ^ Kroutil, J.; Trnka, T.; Cerny, M. (2004). "Improved procedure for the selective N-debenzylation of benzylamines by diisopropyl azodicarboxylate". Synthesis. 3 (3): 446–450. doi:10.1055/s-2004-815937.