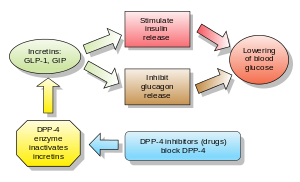
Inhibitors of dipeptidyl peptidase 4 (DPP-4 inhibitors or gliptins) are a class of oral hypoglycemics that block the enzyme dipeptidyl peptidase-4 (DPP-4). They can be used to treat diabetes mellitus type 2.
The first agent of the class – sitagliptin – was approved by the FDA in 2006.[1]
Glucagon increases blood glucose levels, and DPP-4 inhibitors reduce glucagon and blood glucose levels. The mechanism of DPP-4 inhibitors is to increase incretin levels (GLP-1 and GIP),[2][3][4] which inhibit glucagon release, which in turn increases insulin secretion, decreases gastric emptying, and decreases blood glucose levels.
A 2018 meta-analysis found no favorable effect of DPP-4 inhibitors on all-cause mortality, cardiovascular mortality, myocardial infarction or stroke in patients with type 2 diabetes.[5]
- ^ "FDA Approves New Treatment for Diabetes" (Press release). U.S. Food and Drug Administration. October 17, 2006. Retrieved 2006-10-17.
- ^ McIntosh CH, Demuth HU, Pospisilik JA, Pederson R (June 2005). "Dipeptidyl peptidase IV inhibitors: how do they work as new antidiabetic agents?". Regulatory Peptides. 128 (2): 159–65. doi:10.1016/j.regpep.2004.06.001. PMID 15780435. S2CID 9151210.
- ^ Behme MT, Dupré J, McDonald TJ (April 2003). "Glucagon-like peptide 1 improved glycemic control in type 1 diabetes". BMC Endocrine Disorders. 3 (1): 3. doi:10.1186/1472-6823-3-3. PMC 154101. PMID 12697069.
- ^ Dupre J, Behme MT, Hramiak IM, McFarlane P, Williamson MP, Zabel P, McDonald TJ (June 1995). "Glucagon-like peptide I reduces postprandial glycemic excursions in IDDM". Diabetes. 44 (6): 626–30. doi:10.2337/diabetes.44.6.626. PMID 7789625.
- ^ Zheng SL, Roddick AJ, Aghar-Jaffar R, Shun-Shin MJ, Francis D, Oliver N, Meeran K (April 2018). "Association Between Use of Sodium-Glucose Cotransporter 2 Inhibitors, Glucagon-like Peptide 1 Agonists, and Dipeptidyl Peptidase 4 Inhibitors With All-Cause Mortality in Patients With Type 2 Diabetes: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis". JAMA. 319 (15): 1580–1591. doi:10.1001/jama.2018.3024. PMC 5933330. PMID 29677303.