| |

| |

| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
1,1′-Oxydibenzene[1] | |
| Systematic IUPAC name
Phenoxybenzene | |
| Other names | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| 1364620 | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.002.711 |
| EC Number |
|
| 165477 | |
PubChem CID
|
|
| RTECS number |
|
| UNII | |
| UN number | 3077 |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C12H10O | |
| Molar mass | 170.211 g·mol−1 |
| Appearance | Colorless solid or liquid |
| Odor | geranium-like |
| Density | 1.08 g/cm3 (20 °C)[2] |
| Melting point | 25 to 26 °C (77 to 79 °F; 298 to 299 K) |
| Boiling point | 258.55 °C (497.39 °F; 531.70 K)[3] at 100 kPa (1 bar), 121 °C at 1.34 kPa (10.05 mm Hg) |
| Insoluble | |
| Vapor pressure | 0.02 mmHg (25 °C)[2] |
| -108.1·10−6 cm3/mol | |
| Hazards | |
| GHS labelling: | |
  
| |
| Danger | |
| H319, H360Fd, H400, H411 | |
| P264, P273, P280, P305+P351+P338, P337+P313, P391, P501 | |
| NFPA 704 (fire diamond) | |
| Flash point | 115 °C (239 °F; 388 K) |
| Explosive limits | 0.7%–6.0%[2] |
| Lethal dose or concentration (LD, LC): | |
LD50 (median dose)
|
3370 mg/kg (rat, oral) 4000 mg/kg (rat, oral) 4000 mg/kg (guinea pig, oral)[4] |
| NIOSH (US health exposure limits): | |
PEL (Permissible)
|
TWA 1 ppm (7 mg/m3)[2] |
REL (Recommended)
|
TWA 1 ppm (7 mg/m3)[2] |
IDLH (Immediate danger)
|
100 ppm[2] |
| Safety data sheet (SDS) | Aldrich MSDS |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
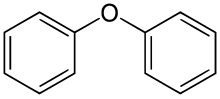
Diphenyl ether is the organic compound with the formula (C6H5)2O. It is a colorless, low-melting solid. This, the simplest diaryl ether, has a variety of niche applications.[5]
- ^ a b c "CHAPTER P-6. Applications to Specific Classes of Compounds". Nomenclature of Organic Chemistry : IUPAC Recommendations and Preferred Names 2013 (Blue Book). Cambridge: The Royal Society of Chemistry. 2014. p. 705. doi:10.1039/9781849733069-00648. ISBN 978-0-85404-182-4.
- ^ a b c d e f NIOSH Pocket Guide to Chemical Hazards. "#0496". National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health (NIOSH).
- ^ Byers, Charles H.; Williams, David F. (July 1987). "Viscosities of pure polyaromatic hydrocarbons". Journal of Chemical & Engineering Data. 32 (3): 344–348. doi:10.1021/je00049a018. ISSN 0021-9568.
- ^ "Phenyl ether". Immediately Dangerous to Life or Health Concentrations (IDLH). National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health (NIOSH).
- ^ Cite error: The named reference
Ullmannwas invoked but never defined (see the help page).
