 | |
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Trade names | Persantine, others |
| AHFS/Drugs.com | Monograph |
| MedlinePlus | a682830 |
| Routes of administration | By mouth, intravenous |
| ATC code | |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status | |
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Bioavailability | 37–66%[1] |
| Protein binding | ~99% |
| Metabolism | Liver (glucuronidation)[2] |
| Elimination half-life | α phase: 40 min, β phase: 10 hours |
| Excretion | Biliary (95%), urine (negligible) |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| IUPHAR/BPS | |
| DrugBank | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.000.340 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
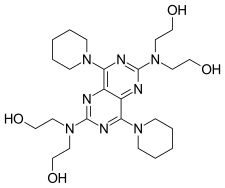
| Formula | C24H40N8O4 |
| Molar mass | 504.636 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
| (verify) | |
Dipyridamole (trademarked as Persantine and others) is a nucleoside transport inhibitor and a PDE3 inhibitor medication that inhibits blood clot formation[3][dead link] when given chronically and causes blood vessel dilation when given at high doses over a short time.
- ^ Nielsen-Kudsk F, Pedersen AK (May 1979). "Pharmacokinetics of dipyridamole". Acta Pharmacologica et Toxicologica. 44 (5): 391–399. doi:10.1111/j.1600-0773.1979.tb02350.x. PMID 474151.
- ^ "Aggrenox (aspirin/extended-release dipyridamole) Capsules. Full Prescribing Information" (PDF). Boehringer Ingelheim Pharmaceuticals, Inc. Retrieved 1 December 2016.
- ^ "Dipyridamole" at Dorland's Medical Dictionary