| |

| |

| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
bis(pentacarbonylrhenium)(Re—Re)
| |
| Other names
Rhenium carbonyl; rhenium pentacarbonyl
| |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.034.714 |
| EC Number |
|
PubChem CID
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| Re2(CO)10 | |
| Molar mass | 652.52 g/mol |
| Melting point | 170 °C (338 °F; 443 K) (decomposes) |
| Hazards[1] | |
| GHS labelling: | |
 
| |
| Danger | |
| H301, H330, H331, H332 | |
| P261, P271, P304+P340+P311, P403+P233, P405, P501 | |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
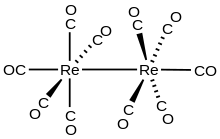
Dirhenium decacarbonyl is the inorganic compound with the chemical formula Re2(CO)10 . Commercially available, it is used as a starting point for the synthesis of many rhenium carbonyl complexes. It was first reported in 1941 by Walter Hieber, who prepared it by reductive carbonylation of rhenium.[2] The compound consists of a pair of square pyramidal Re(CO)5 units joined via a Re-Re bond, which produces a homoleptic carbonyl complex.[3]
- ^ "Dirhenium decacarbonyl". Sigma Aldrich.
- ^ W. Hieber; H. Fuchs (1941). "Über Metallcarbonyle. XXXVIII. Über Rheniumpentacarbonyl". Zeitschrift für anorganische und allgemeine Chemie (in German). 248 (3): 256–268. doi:10.1002/zaac.19412480304.
- ^ F. Armstrong; J. Rourke; M. Hagerman; M. Weller; P. Atkins; T. Overton (2010). "Shiver and Atkins' Inorganic Chemistry 5th edition": 555.
{{cite journal}}: Cite journal requires|journal=(help)