| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
disodium tetracarbonylferrate
| |
| Systematic IUPAC name
disodium tetracarbonylferrate | |
| Other names
disodium iron tetracarbonyl,
Collman's reagent
| |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.035.395 |
| EC Number |
|
PubChem CID
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C4FeNa2O4 | |
| Molar mass | 213.87 |
| Appearance | Colorless solid |
| Density | 2.16 g/cm3, solid |
| Decomposes | |
| Solubility | tetrahydrofuran, dimethylformamide, dioxane |
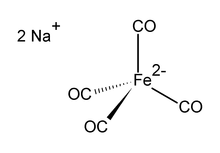
| Structure | |
| Distorted tetrahedron | |
| Tetrahedral | |
| Hazards | |
| Occupational safety and health (OHS/OSH): | |
Main hazards
|
Pyrophoric |
| Related compounds | |
Related compounds
|
Iron pentacarbonyl |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
Disodium tetracarbonylferrate is the organoiron compound with the formula Na2[Fe(CO)4]. It is always used as a solvate, e.g., with tetrahydrofuran or dimethoxyethane, which bind to the sodium cation.[1] An oxygen-sensitive colourless solid, it is a reagent in organometallic and organic chemical research. The dioxane solvated sodium salt is known as Collman's reagent, in recognition of James P. Collman, an early popularizer of its use.[2]
- ^ Strong, H.; Krusic, P. J.; San Filippo, J. (1990). Sodium Carbonyl Ferrates, Na2[Fe(CO)4], Na2[Fe2(CO)8], and Na2[Fe3(CO)11]. Bis[μ-Nitrido-Bis(triphenylphosphorus)1+] Undeca-Carbonyltriferrate2−, [(Ph3P)2N]2[Fe3(CO)11]. Inorganic Syntheses. Vol. 28. pp. 203–207. doi:10.1002/9780470132593.ch52. ISBN 0-471-52619-3.
- ^ Miessler, G. L.; Tarr, D. A. (2004). Inorganic Chemistry. Upper Saddle River, NJ: Pearson.