| |

| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
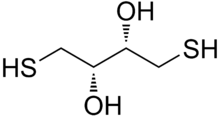
| Preferred IUPAC name
(2S,3S)-1,4-Bis(sulfanyl)butane-2,3-diol | |
| Other names
(2S,3S)-1,4-Dimercaptobutane-2,3-diol
D-threo-1,4-Dimercaptobutane-2,3-diol D-threo-1,4-Dimercapto-2,3-butanediol 1,4-Dithio-D-threitol Cleland's reagent Reductacryl | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
| DrugBank | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.020.427 |
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C4H10O2S2 | |
| Molar mass | 154.253 g/mol |
| Appearance | White solid |
| Melting point | 42 to 43 °C (108 to 109 °F; 315 to 316 K) |
| Boiling point | 125 to 130 °C (257 to 266 °F; 398 to 403 K) at 2 mmHg |
| Soluble | |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
Dithiothreitol (DTT) is an organosulfur compound with the formula (CH(OH)CH2SH)2. A colorless compound, it is classified as a dithiol and a diol. DTT is redox reagent also known as Cleland's reagent, after W. Wallace Cleland.[2] The reagent is commonly used in its racemic form. Its name derives from the four-carbon sugar, threose. DTT has an epimeric ('sister') compound, dithioerythritol (DTE).
- ^ O'Neil MJ, ed. (2001). Merck Index : an encyclopedia of chemicals, drugs, & biologicals (13th ed.). United States: Merck & Co, Inc. ISBN 0-911910-13-1.
- ^ Cleland WW (April 1964). "Dithiothreitol, a New Protective Reagent for SH Groups". Biochemistry. 3 (4): 480–2. doi:10.1021/bi00892a002. PMID 14192894.