 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| AHFS/Drugs.com | International Drug Names |
| ATC code | |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| ChEMBL | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
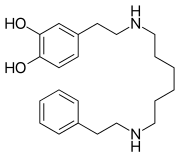
| Formula | C22H32N2O2 |
| Molar mass | 356.510 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
| (verify) | |
Dopexamine is a synthetic analogue of dopamine that is administered intravenously in hospitals to reduce exacerbations of heart failure and to treat heart failure following cardiac surgery. It is not used often, as more established drugs like epinephrine, dopamine, dobutamine, norepinephrine, and levosimendan work as well. It works by stimulating beta-2 adrenergic receptors and peripheral dopamine receptor D1 and dopamine receptor D2. It also inhibits the neuronal re-uptake of norepinephrine.
The most common adverse effects include fast heart beats and nausea.
It was discovered by scientists at Fisons, which licensed it to Ipsen in 1993, and Ipsen in turn licensed it to Élan in 1999. Ipsen licensed rights in North America and Japan to Circassia in 2008; the drug had never been approved in those countries. Dopexamine went off-patent in 2010.