 | |
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Routes of administration | Oral |
| ATC code | |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status |
|
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Metabolism | Hepatic |
| Elimination half-life | 3-4 hours[1] |
| Excretion | Renal |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| ChEMBL | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
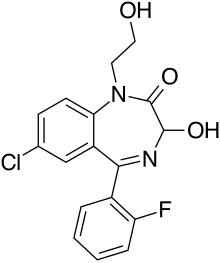
| Formula | C17H14ClFN2O3 |
| Molar mass | 348.76 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
| | |
Doxefazepam (marketed under brand name Doxans) is a benzodiazepine medication It possesses anxiolytic, anticonvulsant, sedative and skeletal muscle relaxant properties. It is used therapeutically as a hypnotic.[2] According to Babbini and colleagues in 1975, this derivative of flurazepam was between 2 and 4 times more potent than the latter while at the same time being half as toxic in laboratory animals.[3]
It was patented in 1972 and came into medical use in 1984.[4]
- ^ "Doxefazepam". IPCS INTOX. Archived from the original on 24 July 2008.
- ^ Rodriguez G, Rosadini G, Sannita WG, Strumia E (1984). "Effects of doxefazepam on normal sleep. An EEG and neuropsychological study". Neuropsychobiology. 11 (2): 133–139. doi:10.1159/000118066. PMID 6483162.
- ^ Babbini M, Torrielli MV, Strumia E, Gaiardi M, Bartoletti M, De Marchi F (August 1975). "Sedative-hypnotic properties of a new benzodiazepine in comparison with flurazepam. Pharmacological and clinical findings". Arzneimittel-Forschung. 25 (8): 1294–1300. PMID 241364.
- ^ Fischer J, Ganellin CR (2006). Analogue-based Drug Discovery. John Wiley & Sons. p. 539. ISBN 9783527607495.