 | |
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Pronunciation | Droe-SPY-re-nown |
| Trade names | Alone: Slynd With estradiol: Angeliq With ethinylestradiol: Yasmin, Yasminelle, Yaz, others With estetrol: Nextstellis |
| Other names | Dihydrospirenone; Dihydrospirorenone; 1,2-Dihydrospirorenone; MSp; SH-470; ZK-30595; LF-111; 17β-Hydroxy-6β,7β:15β,16β-dimethylene-3-oxo-17α-pregn-4-ene-21-carboxylic acid, γ-lactone |
| AHFS/Drugs.com | Professional Drug Facts |
| License data |
|
| Routes of administration | By mouth[1] |
| Drug class | Progestogen; Progestin; Antimineralocorticoid; Steroidal antiandrogen |
| ATC code | |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status | |
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Bioavailability | 66–85%[1][4][5] |
| Protein binding | 95–97% (to albumin)[3][1][4] |
| Metabolism | Liver (mostly CYP450-independent (reduction, sulfation, and cleavage of lactone ring), some CYP3A4 contribution)[4][6][7][8] |
| Metabolites | • Drospirenone acid[3] • 4,5-Dihydrodrospirenone 3-sulfate[3] |
| Elimination half-life | 25–33 hours[3][4][1] |
| Excretion | Urine, feces[3] |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| DrugBank | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.060.599 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
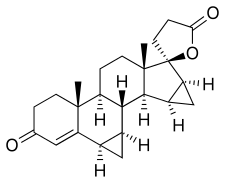
| Formula | C24H30O3 |
| Molar mass | 366.501 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
| (verify) | |
Drospirenone is a progestin and antiandrogen medication which is used in birth control pills to prevent pregnancy and in menopausal hormone therapy, among other uses.[1][9] It is available both alone under the brand name Slynd and in combination with an estrogen under the brand name Yasmin among others.[9][3] The medication is an analog of the drug spironolactone.[10] Drospirenone is taken by mouth.[1][3]
Common side effects include acne, headache, breast tenderness, weight increase, and menstrual changes.[3] Rare side effects may include high potassium levels and blood clots (when taken as a combined oestrogen-progestogen pill), among others.[3][11] Drospirenone is a progestin, or a synthetic progestogen, and hence is an agonist of the progesterone receptor, the biological target of progestogens like progesterone.[1] It has additional antimineralocorticoid and antiandrogenic activity and no other important hormonal activity.[1] Because of its antimineralocorticoid activity and lack of undesirable off-target activity, drospirenone is said to more closely resemble bioidentical progesterone than other progestins.[12][13]
Drospirenone was patented in 1976 and introduced for medical use in 2000.[14][15] It is available widely throughout the world.[9] The medication is sometimes referred to as a "fourth-generation" progestin.[16][17] It is available as a generic medication.[18] In 2020, a formulation of drospirenone with ethinylestradiol was the 145th most commonly prescribed medication in the United States, with more than 4 million prescriptions.[19][20]
- ^ a b c d e f g h Kuhl H (August 2005). "Pharmacology of estrogens and progestogens: influence of different routes of administration". Climacteric. 8 Suppl 1 (sup1): 3–63. doi:10.1080/13697130500148875. PMID 16112947. S2CID 24616324.
- ^ "Health product highlights 2021: Annexes of products approved in 2021". Health Canada. 3 August 2022. Retrieved 25 March 2024.
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j Slynd-drospirenone tablet, film coated drug label/data at DailyMed from U.S. National Library of Medicine, National Institutes of Health.
- ^ a b c d Krattenmacher R (July 2000). "Drospirenone: pharmacology and pharmacokinetics of a unique progestogen". Contraception. 62 (1): 29–38. doi:10.1016/S0010-7824(00)00133-5. PMID 11024226.
- ^ Stanczyk FZ, Hapgood JP, Winer S, Mishell DR (April 2013). "Progestogens used in postmenopausal hormone therapy: differences in their pharmacological properties, intracellular actions, and clinical effects". Endocrine Reviews. 34 (2): 171–208. doi:10.1210/er.2012-1008. PMC 3610676. PMID 23238854.
- ^ Gaspard U, Endrikat J, Desager JP, Buicu C, Gerlinger C, Heithecker R (April 2004). "A randomized study on the influence of oral contraceptives containing ethinylestradiol combined with drospirenone or desogestrel on lipid and lipoprotein metabolism over a period of 13 cycles". Contraception. 69 (4): 271–278. doi:10.1016/j.contraception.2003.11.003. PMID 15033400.
- ^ Bachmann G, Kopacz S (November 2009). "Drospirenone/ethinyl estradiol 3 mg/20 mug (24/4 day regimen): hormonal contraceptive choices - use of a fourth-generation progestin". Patient Preference and Adherence. 3: 259–264. doi:10.2147/PPA.S3901. PMC 2778416. PMID 19936169.
- ^ Wiesinger H, Berse M, Klein S, Gschwend S, Höchel J, Zollmann FS, et al. (December 2015). "Pharmacokinetic interaction between the CYP3A4 inhibitor ketoconazole and the hormone drospirenone in combination with ethinylestradiol or estradiol". British Journal of Clinical Pharmacology. 80 (6): 1399–1410. doi:10.1111/bcp.12745. PMC 4693482. PMID 26271371.
- ^ a b c Cite error: The named reference
Drugs.comwas invoked but never defined (see the help page). - ^ Krattenmacher R (July 2000). "Drospirenone: pharmacology and pharmacokinetics of a unique progestogen". Contraception. 62 (1): 29–38. doi:10.1016/S0010-7824(00)00133-5. PMID 11024226.
- ^ Cite error: The named reference
pmid26598309was invoked but never defined (see the help page). - ^ Oelkers W (December 2000). "Drospirenone--a new progestogen with antimineralocorticoid activity, resembling natural progesterone". The European Journal of Contraception & Reproductive Health Care (Review). 5 (Suppl 3): 17–24. doi:10.1080/14730782.2000.12288986. PMID 11246598. S2CID 35051390.
- ^ Oelkers W (December 2002). "Antimineralocorticoid activity of a novel oral contraceptive containing drospirenone, a unique progestogen resembling natural progesterone". The European Journal of Contraception & Reproductive Health Care (Review). 7 (Suppl 3): 19–26, discussion 42–3. doi:10.1080/14730782.2000.12288986. PMID 12659403.
- ^ Cite error: The named reference
Ravina2011was invoked but never defined (see the help page). - ^ Alapi EM, Fischer J (2006). "Part III: Table of Selected Analogue Classes". In Fischer J, Ganellin CR (eds.). Analogue-based Drug Discovery. John Wiley & Sons. p. 459. ISBN 978-3-527-60749-5.
- ^ Cite error: The named reference
HatcherM.D.2007was invoked but never defined (see the help page). - ^ Cite error: The named reference
RossoZeichner2016was invoked but never defined (see the help page). - ^ Generic Yasmin Availability via yasminat Drugs.com
- ^ "The Top 300 of 2020". ClinCalc. Retrieved 7 October 2022.
- ^ "Drospirenone; Ethinyl Estradiol - Drug Usage Statistics". ClinCalc. Retrieved 7 October 2022.