This article is missing information about consensus cystine repeat, difulfide bond position (residues, inter/intra?). (March 2019) |
| EGF-like domain | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
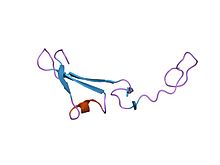 Structure of the epidermal growth factor-like domain of heregulin-alpha.[1] | |||||||||
| Identifiers | |||||||||
| Symbol | EGF | ||||||||
| Pfam | PF00008 | ||||||||
| Pfam clan | CL0001 | ||||||||
| ECOD | 389.1.1 | ||||||||
| InterPro | IPR000742 | ||||||||
| PROSITE | PDOC00021 | ||||||||
| SCOP2 | 1apo / SCOPe / SUPFAM | ||||||||
| CDD | cd00053 | ||||||||
| |||||||||
| EGF-like domain, extracellular | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 crystal structure of the extracellular segment of integrin alphavbeta3 | |||||||||
| Identifiers | |||||||||
| Symbol | EGF_2 | ||||||||
| Pfam | PF07974 | ||||||||
| Pfam clan | CL0001 | ||||||||
| InterPro | IPR013111 | ||||||||
| CDD | cd00054 | ||||||||
| |||||||||
The EGF-like domain is an evolutionary conserved protein domain, which derives its name from the epidermal growth factor where it was first described. It comprises about 30 to 40 amino-acid residues and has been found in a large number of mostly animal proteins.[2][3] Most occurrences of the EGF-like domain are found in the extracellular domain of membrane-bound proteins or in proteins known to be secreted. An exception to this is the prostaglandin-endoperoxide synthase. The EGF-like domain includes 6 cysteine residues which in the epidermal growth factor have been shown to form 3 disulfide bonds. The structures of 4-disulfide EGF-domains have been solved from the laminin and integrin proteins. The main structure of EGF-like domains is a two-stranded β-sheet followed by a loop to a short C-terminal, two-stranded β-sheet. These two β-sheets are usually denoted as the major (N-terminal) and minor (C-terminal) sheets.[4] EGF-like domains frequently occur in numerous tandem copies in proteins: these repeats typically fold together to form a single, linear solenoid domain block as a functional unit.
- ^ Nagata K, Kohda D, Hatanaka H, et al. (August 1994). "Solution structure of the epidermal growth factor-like domain of heregulin-alpha, a ligand for p180erbB-4". EMBO J. 13 (15): 3517–23. doi:10.1002/j.1460-2075.1994.tb06658.x. PMC 395255. PMID 8062828.
- ^ Downing AK, Knott V, Werner JM, Cardy CM, Campbell ID, Handford PA (May 1996). "Solution structure of a pair of calcium-binding epidermal growth factor-like domains: implications for the Marfan syndrome and other genetic disorders". Cell. 85 (4): 597–605. doi:10.1016/S0092-8674(00)81259-3. PMID 8653794. S2CID 15410014.
- ^ Bork P, Downing AK, Kieffer B, Campbell ID (May 1996). "Structure and distribution of modules in extracellular proteins". Q. Rev. Biophys. 29 (2): 119–67. doi:10.1017/S0033583500005783. PMID 8870072. S2CID 6104446.
- ^ Wouters MA, Rigoutsos I, Chu CK, Feng LL, Sparrow DB, Dunwoodie SL (2005). "Evolution of distinct EGF domains with specific functions". Protein Science. 14 (4): 1091–103. doi:10.1110/ps.041207005. PMC 2253431. PMID 15772310.