You can help expand this article with text translated from the corresponding article in Chinese. (October 2021) Click [show] for important translation instructions.
|
This article needs additional citations for verification. (October 2012) |
East China | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Country | |
| Area | |
| • Total | 795,837 km2 (307,274 sq mi) |
| Population | 384,364,968 |
| • Density | 483/km2 (1,250/sq mi) |
| GDP | 2022[2] |
| - Total | ¥46.291 trillion $6.883 trillion (excluding Taiwan) |
| - Per Capita | ¥120,435 $17,810 (excluding Taiwan) |
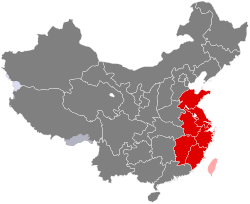
East China (华东) is a region in the People's Republic of China. It mainly consists of seven provincial administrative regions, namely Shanghai, Jiangsu, Zhejiang, Anhui, Fujian, Jiangxi, and Shandong.
A concept abolished in 1978, for economical purposes the region was defined from 1949 to 1961 by the Chinese Central Government to include the provinces of (in alphabetical order) Anhui, Fujian, Jiangsu, Shandong and Zhejiang, as well as the municipality of Shanghai. In 1961, the province of Jiangxi was added to the region (previously it was considered part of South Central China).
Since the Chinese government claims Taiwan and the few outlying islands of Fujian (Kinmen and Matsu) governed by the Republic of China (Taiwanese government) as its territory, the claimed "Taiwan Province, People's Republic of China" is also classified in this region.
- ^ "Main Data of the Seventh National Population Census". National Bureau of Statistics of China. Archived from the original on May 11, 2021.
- ^ GDP-2022 is a preliminary data "Home - Regional - Quarterly by Province" (Press release). China NBS.