 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| AHFS/Drugs.com | International Drug Names |
| Routes of administration | Oral |
| ATC code | |
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Protein binding | Greater than 95% |
| Metabolism | Hepatic (CYP3A4-mediated), to carebastine |
| Elimination half-life | 15 to 19 hours (carebastine) |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| ChEMBL | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.106.831 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
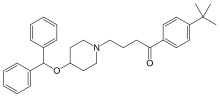
| Formula | C32H39NO2 |
| Molar mass | 469.669 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
| (verify) | |
Ebastine is a H1 antihistamine with low potential for causing drowsiness.
It does not penetrate the blood–brain barrier to a significant amount and thus combines an effective block of the H1 receptor in peripheral tissue with a low incidence of central side effects, i.e. seldom causing sedation or drowsiness.[1][2][3]
It was patented in 1983 by Almirall S.A and came into medical use in 1990.[4] The substance is often provided in micronised form due to poor water solubility.
- ^ Cite error: The named reference
Tagawa 2001was invoked but never defined (see the help page). - ^ Cite error: The named reference
Arzneistoff-Profilewas invoked but never defined (see the help page). - ^ Cite error: The named reference
Bousquet 1999was invoked but never defined (see the help page). - ^ Fischer J, Ganellin CR (2006). Analogue-based Drug Discovery. John Wiley & Sons. p. 549. ISBN 9783527607495.