| Ebola River | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Native name | Legbala (Northern Ngbandi) |
| Location | |
| Country | Democratic Republic of the Congo |
| Physical characteristics | |
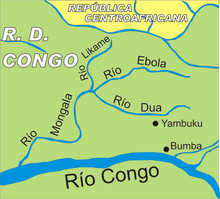
| Mouth | Mongala River |
• coordinates | 3°19′24″N 20°57′38″E / 3.32333°N 20.96056°E |
| Length | 250 km (160 mi) |
The Ebola River (/iˌboʊlə/ or /əˈboʊlə/),[1][2] also commonly known by its Ngbandi name Legbala,[3] is the headstream of the Mongala River, a tributary of the Congo River, in northern Democratic Republic of the Congo.[4] It is roughly 250 kilometers (160 mi) in length.[citation needed]
The name Ebola is a French corruption of Legbala, its name in Ngbandi which means 'white water'.[5] During the Belgian administration these names were interchangeable along with the French names Eau Blanche[3] and rarely L'Ébola.[5]
In 1976, Ebola virus was first identified in Yambuku, 111 kilometers (69 mi) from the Ebola River, but the virologist Karl Johnson decided to name it after the river so that the town would not be associated with the disease's stigma.[5] Thus, the river is eponymous to the terms Ebola virus, Ebolavirus, and Ebola virus disease (usually referred to as simply "Ebola").[6]
- ^ "The American Heritage Dictionary entry: Ebola". The American Heritage Dictionary. Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Publishing Company. Archived from the original on 2021-07-29. Retrieved 2020-04-15.
- ^ "Ebola | meaning in the Cambridge English Dictionary". Cambridge English Dictionary. Archived from the original on 2018-01-24. Retrieved 2020-04-15.
- ^ a b Tanghe, Basile; Vangele, A. (June 1939). "Région de la Haute Ebola: Notes d'histoire (1890-1900)" (PDF). Aequatoria (in French). 2 (6): 61–65. JSTOR 25837382. Archived (PDF) from the original on 2020-07-11. Retrieved 2020-02-03.
- ^
vanden Bossche, J.-P.; Bernacsek, G. M. (1990). Zaire. Vol. 1. p. 336. ISBN 9789251029831. Retrieved 31 July 2014.
{{cite book}}:|journal=ignored (help) - ^ a b c Wordsworth, Dot (25 October 2014). "How Ebola got its name". The Spectator. Archived from the original on 1 December 2019. Retrieved 26 October 2014.
- ^ "Ebola outbreak confirmed by DR Congo". BBC News. 2014-08-25. Archived from the original on 2018-12-28. Retrieved 2018-06-21.