| Echinostoma | |
|---|---|
| |
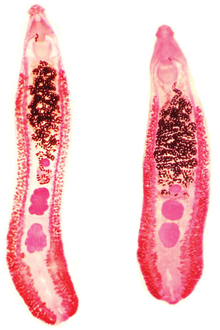
| Two specimens of Echinostoma revolutum | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Domain: | Eukaryota |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Platyhelminthes |
| Class: | Trematoda |
| Order: | Plagiorchiida |
| Family: | Echinostomatidae |
| Subfamily: | Echinostomatinae |
| Genus: | Echinostoma Rudolphi, 1809[1] |
Echinostoma is a genus of trematodes (flukes), which can infect both humans and other animals. These intestinal flukes have a three-host life cycle with snails or other aquatic organisms as intermediate hosts,[2] and a variety of animals, including humans, as their definitive hosts.
Echinostoma infect the gastrointestinal tract of humans, and can cause a disease known as echinostomiasis. The parasites are spread when humans or animals eat infected raw or undercooked food, such as bivalve molluscs or fish. [3]
- ^ Rudolphi K. (1809). Entoz. Hist. Nat. 2(1): 38.
- ^ Pantoja, Camila; Faltýnková, Anna; O’Dwyer, Katie; Jouet, Damien; Skírnisson, Karl; Kudlai, Olena (2021). "Diversity of echinostomes (Digenea: Echinostomatidae) in their snail hosts at high latitudes". Parasite. 28: 59. doi:10.1051/parasite/2021054. ISSN 1776-1042. PMC 8336728.

- ^ Cite error: The named reference
Toledo2012was invoked but never defined (see the help page).