 | |
| Feature type | valley network[1] |
|---|---|
| Location | Arcadia quadrangle |
| Coordinates | 36°41′N 266°54′E / 36.68°N 266.9°E |
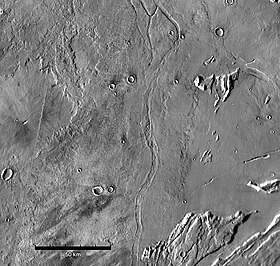
Enipeus Vallis is a valley in the northern hemisphere of the planet Mars. It is centered at lat. 37°N, long. 267°E in the Arcadia quadrangle (MC-3) between the large volcano Alba Mons and the Tempe Terra plateau. The valley follows a gently sinuous, north–south path for a distance of about 357 km (222 mi).[2] It is likely an ancient watercourse that formed during the early Hesperian (or late Noachian) period,[3] around 3.7 billion years ago.[4]
The valley is named after a river in Thessaly, Greece. Enipeus is also the name of a river god in classical mythology.[5] The International Astronomical Union (IAU) formally adopted the name Enipeus Vallis in 1991.[2] Vallis is the Latin word for valley.[6]
- ^ Carr, M.H. (1995). The Martian Drainage System and the Origin of Valley Networks and Fretted Channels. J. Geophys. Res., 100(E4), p. 7491, Fig. 9a.
- ^ a b USGS Gazetteer of Planetary Nomenclature. http://planetarynames.wr.usgs.gov/Feature/1803.
- ^ Moore, H.J. (2001). Geologic Map of the Tempe-Mareotis Region of Mars. USGS Geologic Investigations Series I-2727. http://geopubs.wr.usgs.gov/i-map/i2727/.
- ^ Hartmann, W.K. (2005). Martian Cratering 8: Isochron Refinement and the Chronology of Mars. Icarus, 174, p. 317, Tbl. 3. doi:10.1016/j.icarus.2004.11.023.
- ^ Simpson, D.P. (1968). Cassell's New Latin Dictionary; Funk & Wagnalls: New York, p. 215.
- ^ USGS Gazetteer of Planetary Nomenclature. Descriptor Terms. http://planetarynames.wr.usgs.gov/DescriptorTerms.