| Observation data Epoch J2000.0 Equinox J2000.0 (ICRS) | |
|---|---|
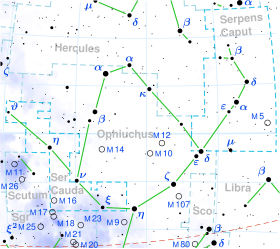
| Constellation | Serpens |
| Right ascension | 15h 50m 48.96622s[1] |
| Declination | +04° 28′ 39.8311″[1] |
| Apparent magnitude (V) | +3.69[2] |
| Characteristics | |
| Spectral type | kA2hA5mA7 V[3] |
| U−B color index | +0.12[2] |
| B−V color index | +0.14[2] |
| Astrometry | |
| Radial velocity (Rv) | −9.4±0.6[4] km/s |
| Proper motion (μ) | RA: +128.19[1] mas/yr Dec.: +62.16[1] mas/yr |
| Parallax (π) | 46.30 ± 0.19 mas[1] |
| Distance | 70.4 ± 0.3 ly (21.60 ± 0.09 pc) |
| Absolute magnitude (MV) | +2.04[5] |
| Details | |
| Mass | 1.820±0.026[6] M☉ |
| Radius | 1.783±0.040[6] R☉ |
| Luminosity | 12.134±0.296[6] L☉ |
| Surface gravity (log g) | 4.346[7] cgs |
| Temperature | 7,928±88[7] K |
| Metallicity [Fe/H] | +0.38[7] dex |
| Rotational velocity (v sin i) | 33.1[7] km/s |
| Age | 500±200[6] Myr |
| Other designations | |
| Database references | |
| SIMBAD | data |
Epsilon Serpentis, Latinized from ε Serpentis, is a single,[9] white-hued star in the constellation Serpens, in its head (Serpens Caput). It is visible to the naked eye with an apparent visual magnitude of +3.69.[2] Based upon an annual parallax shift of 46.30 mas as seen from Earth,[1] it is located 70 light years from the Sun. It is moving closer to the Sun with a radial velocity of −9 km/s.[4]
This is an Am star[10] on the main-sequence with a stellar classification of kA2hA5mA7 V.[3] This notation indicates the spectrum displays the calcium K-line of an A2 star, the hydrogen lines of an A5 star, and the metal lines of an A7 star.[11] It has been examined for the presence of a magnetic field, but the detected level was not statistically significant.[12]
Epsilon Serpentis has an estimated 1.82 times the mass of the Sun and 1.78 times the Sun's radius.[6] The star is radiating 12[6] times the Sun's luminosity from its photosphere at an effective temperature of around 7,928 K.[7] It is a candidate for an infrared excess at a wavelength of 25 μm, suggesting a circumstellar disk of dust with a temperature of 250±70 K may be orbiting roughly 4.2 AU from the host star.[13] The star is around half[6] a billion years old and is spinning with a projected rotational velocity of 33.1 km/s.[7]
- ^ a b c d e f Cite error: The named reference
vanLeeuwen2007was invoked but never defined (see the help page). - ^ a b c d Cite error: The named reference
feinstein1974was invoked but never defined (see the help page). - ^ a b Cite error: The named reference
Gray2006was invoked but never defined (see the help page). - ^ a b Cite error: The named reference
deBruijne2012was invoked but never defined (see the help page). - ^ Cite error: The named reference
Anderson2012was invoked but never defined (see the help page). - ^ a b c d e f g Cite error: The named reference
Boyajian2012was invoked but never defined (see the help page). - ^ a b c d e f Cite error: The named reference
David2015was invoked but never defined (see the help page). - ^ Cite error: The named reference
SIMBADwas invoked but never defined (see the help page). - ^ Cite error: The named reference
Rodriguez2015was invoked but never defined (see the help page). - ^ Cite error: The named reference
Adelman1998was invoked but never defined (see the help page). - ^ Cite error: The named reference
Walker2017was invoked but never defined (see the help page). - ^ Cite error: The named reference
Shorlin2002was invoked but never defined (see the help page). - ^ Cite error: The named reference
Smith2010was invoked but never defined (see the help page).