| Erector spinae | |
|---|---|
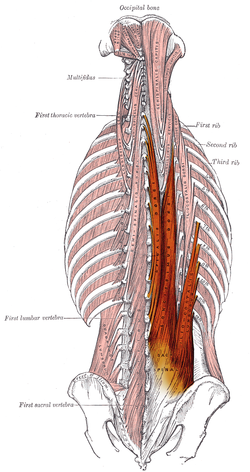 The erector spinae muscle group | |
| Details | |
| Origin | Spinous processes of T9-T12 thoracic vertebrae, medial slope of the dorsal segment of iliac crest |
| Insertion | Spinous processes of T1 and T2 thoracic vertebrae and the cervical vertebrae |
| Artery | Lateral sacral artery |
| Nerve | Posterior branch of spinal nerve |
| Actions | Extends the vertebral column |
| Antagonist | Rectus abdominis muscle |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | musculus erector spinae |
| TA98 | A04.3.02.002 |
| TA2 | 2254 |
| FMA | 71302 |
| Anatomical terms of muscle | |
The erector spinae (/ɪˈrɛktər ˈspaɪni/ irr-EK-tər SPY-nee)[1] or spinal erectors is a set of muscles that straighten and rotate the back. The spinal erectors work together with the glutes (gluteus maximus, gluteus medius and gluteus minimus) to maintain stable posture standing or sitting.
- ^ "How to pronounce spinae in English". Cambridge University Press 2015. Retrieved 10 December 2015.