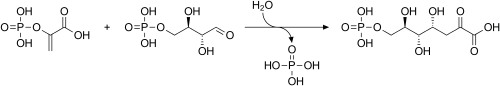| |

| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
(2R,3R)-2,3-dihydroxy-4-oxobutyl phosphate
| |
| Other names
E4P
| |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChEBI | |
| ChemSpider | |
| MeSH | erythrose+4-phosphate |
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C4H9O7P | |
| Molar mass | 200.084 g/mol |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
Erythrose 4-phosphate is a phosphate of the simple sugar erythrose. It is an intermediate in the pentose phosphate pathway and the Calvin cycle.[1]
The enzyme transaldolase catalyzes the formation of erythrose 4-phosphate and fructose 6-phosphate from sedoheptulose 7-phosphate and glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate.[2] This reaction is a part of the non-oxidative phase of the pentose phosphate pathway.
In the Calvin cycle, the enzyme fructose-bisphosphate aldolase catalyzes the formation of sedoheptulose 1,7-bisphosphate from erythrose 4-phosphate and dihydroxyacetone phosphate.[3]
In addition, it serves as a precursor in the biosynthesis of the aromatic amino acids tyrosine, phenylalanine, and tryptophan. It is used in the first step of the shikimate pathway. At this stage, phosphoenolpyruvate and erythrose-4-phosphate react to form 3-deoxy-D-arabinoheptulosonate-7-phosphate (DAHP), in a reaction catalyzed by the enzyme DAHP synthase.
It also used in 3-hydroxy-1-aminoacetone phosphate biosynthesis, which is a precursor of vitamin B6 in DXP-dependent pathway. Erythrose-4-phosphate dehydrogenase is used to produce erythronate-4-phosphate.
- ^ Schramm, M.; Racker, E. (1957). "Formation of Erythrose-4-phosphate and Acetyl Phosphate by a Phosphorolytic Cleavage of Fructose-6-phosphate". Nature. 179 (4574): 1349–1350. Bibcode:1957Natur.179.1349S. doi:10.1038/1791349a0. PMID 13451617. S2CID 1541286.
- ^ Wamelink, M. M. C.; Struys, E. A.; Jakobs, C. (December 2008). "The biochemistry, metabolism and inherited defects of the pentose phosphate pathway: A review". Journal of Inherited Metabolic Disease. 31 (6): 703–717. doi:10.1007/s10545-008-1015-6. ISSN 0141-8955. PMID 18987987.
- ^ Stincone, Anna; Prigione, Alessandro; Cramer, Thorsten; Wamelink, Mirjam M. C.; Campbell, Kate; Cheung, Eric; Olin-Sandoval, Viridiana; Grüning, Nana-Maria; Krüger, Antje; Tauqeer Alam, Mohammad; Keller, Markus A.; Breitenbach, Michael; Brindle, Kevin M.; Rabinowitz, Joshua D.; Ralser, Markus (August 2015). "The return of metabolism: biochemistry and physiology of the pentose phosphate pathway". Biological Reviews. 90 (3): 927–963. doi:10.1111/brv.12140. ISSN 1464-7931. PMC 4470864. PMID 25243985.