| Ethmoidal labyrinth | |
|---|---|
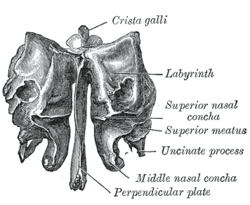 Ethmoid bone from behind. | |
| Details | |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | labyrinthus ethmoidalis |
| TA98 | A02.1.07.007 |
| TA2 | 727 |
| FMA | 57448 |
| Anatomical terms of bone | |
The ethmoidal labyrinth or lateral mass of the ethmoid bone consists of a number of thin-walled cellular cavities, the ethmoid air cells, arranged in three groups, anterior, middle, and posterior, and interposed between two vertical plates of bone; the lateral plate forms part of the orbit, the medial plate forms part of the nasal cavity. In the disarticulated bone many of these cells are opened into, but when the bones are articulated, they are closed in at every part, except where they open into the nasal cavity.[1]