| |
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
Azidoethane | |
| Other names
Ethane, azido-; 1-Azidoethane
| |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChemSpider | |
PubChem CID
|
|
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
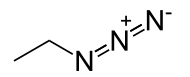
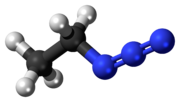
| CH3CH2N3 | |
| Molar mass | 71.083 g·mol−1 |
| Appearance | liquid |
| Boiling point | 50 |
| Explosive data | |
| Shock sensitivity | High |
| Friction sensitivity | High |
| Thermochemistry | |
Std enthalpy of
formation (ΔfH⦵298) |
266.872 |
| Hazards | |
| Occupational safety and health (OHS/OSH): | |
Main hazards
|
Harmful, Explosive |
| Related compounds | |
Related compounds
|
Hydrazoic acid, Chlorine azide, Methyl azide |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
Ethyl azide (CH3CH2N3) is an explosive compound sensitive to rapid heating, shock or impact. It has exploded when heated to room temperature.[1][2] When heated to decomposition it emits toxic fumes of NOx.[3][4]
It is irritating to eyes, respiratory system and skin.
- ^ Campbell, H. C.; Rice, O. K. (1935). "The Explosion of Ethyl Azide". Journal of the American Chemical Society. 57 (6): 1044–1050. doi:10.1021/ja01309a019.
- ^ Rice, O. K.; Campbell, H. C. (1939). "The Explosion of Ethyl Azide in the Presence of Diethyl Ether". The Journal of Chemical Physics. 7 (8): 700–709. Bibcode:1939JChPh...7..700R. doi:10.1063/1.1750516.
- ^ Rice, O. K. (1940). "The Role of Heat Conduction in Thermal Gaseous Explosions". The Journal of Chemical Physics. 8 (9): 727–733. Bibcode:1940JChPh...8..727R. doi:10.1063/1.1750808.
- ^ Costa Cabral, B. J.; Costa, M. L.; Almoster Ferreira, M. A. (2010). "ChemInform Abstract: Molecular Structure and Ionization Energies of Azides: An ab initio Study of Hydrazoic Acid, Methyl Azide and Ethyl Azide". ChemInform. 24 (37): no. doi:10.1002/chin.199337053.