| Euglenozoa Temporal range:
| |
|---|---|
| |
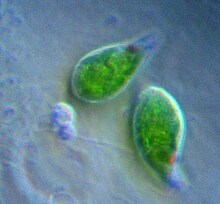
| Two Euglena | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Domain: | Eukaryota |
| Clade: | Discoba |
| Superphylum: | Discicristata |
| Phylum: | Euglenozoa Cavalier-Smith, 1981[2] |
| Classes | |
Euglenozoa are a large group of flagellate Discoba. They include a variety of common free-living species, as well as a few important parasites, some of which infect humans. Euglenozoa are represented by four major groups, i.e., Kinetoplastea, Diplonemea, Euglenida, and Symbiontida. Euglenozoa are unicellular, mostly around 15–40 μm (0.00059–0.00157 in) in size, although some euglenids get up to 500 μm (0.020 in) long.[3]
- ^ Zakryś, B; Milanowski, R; Karnkowska, Anna (2017). "Evolutionary Origin of Euglena". Euglena: Biochemistry, Cell and Molecular Biology. Advances in Experimental Medicine and Biology. Vol. 979. pp. 3–17. doi:10.1007/978-3-319-54910-1_1. ISBN 978-3-319-54908-8. PMID 28429314.
- ^ Cavalier-Smith T (1981). "Eukaryote kingdoms: seven or nine?". Bio Systems. 14 (3–4): 461–481. doi:10.1016/0303-2647(81)90050-2. PMID 7337818.
- ^ "Euglenozoa". Encyclopedia of Life. National Museum of Natural History - Smithsonian Institution. Retrieved 16 January 2020.