| Experimental Advanced Superconducting Tokamak | |
|---|---|
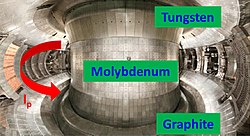 EAST vacuum vessel | |
| Device type | Tokamak |
| Location | Hefei, China |
| Affiliation | Hefei Institutes of Physical Science, Chinese Academy of Sciences |
| Technical specifications | |
| Major radius | 1.85 m (6 ft 1 in) |
| Minor radius | 0.45 m (1 ft 6 in) |
| Magnetic field | 3.5 T (35,000 G) |
| Heating power | 7.5 MW |
| Discharge duration | 102 s |
| Plasma current | 1.0 MA |
| Plasma temperature | 100×106 K |
| History | |
| Year(s) of operation | 2006–present |
| Preceded by | HT-6M |
| Experimental Advanced Superconducting Tokamak | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Chinese | 先进超导托卡马克实验装置 | ||||||
| Hanyu Pinyin | xiānjìn chāodǎo tuōkǎmǎkè shíyàn zhuāngzhì | ||||||
| Literal meaning | Advanced Superconducting Tokamak Experimental device | ||||||
| |||||||

The Experimental Advanced Superconducting Tokamak (EAST), internal designation HT-7U (Hefei Tokamak 7 Upgrade), is an experimental superconducting tokamak magnetic fusion energy reactor in Hefei, China. The Hefei Institutes of Physical Science is conducting the experiment for the Chinese Academy of Sciences. It has operated since 2006.
It is the first tokamak to employ superconducting toroidal and poloidal magnets. It aims for plasma pulses of up to 1,000 seconds.
Since China is a member of the international ITER project, it is hoped that EAST will provide new impetus for its further development.