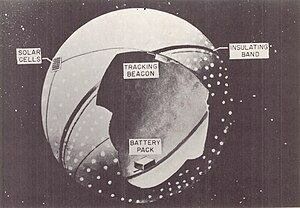
 Cutaway diagram of Explorer 19 | |
| Names | AD-A Air Density experiment-A |
|---|---|
| Mission type | Air density |
| Operator | NASA |
| COSPAR ID | 1963-053A |
| SATCAT no. | 00714 |
| Spacecraft properties | |
| Spacecraft | Explorer XIX |
| Spacecraft type | Air Density Explorer |
| Bus | AD-A |
| Manufacturer | Langley Research Center |
| Launch mass | 7.7 kg (17 lb) |
| Dimensions | 3.66 m (12.0 ft) diameter |
| Power | Solar cells and Rechargeable batteries |
| Start of mission | |
| Launch date | 19 December 1963, 18:49:25 GMT |
| Rocket | Scout X-4 (S-122R) |
| Launch site | Vandenberg, PALC-D |
| Contractor | Vought |
| Entered service | 19 December 1963 |
| End of mission | |
| Decay date | 10 May 1981 |
| Orbital parameters | |
| Reference system | Geocentric orbit |
| Regime | Low Earth orbit |
| Perigee altitude | 590 km (370 mi) |
| Apogee altitude | 2,394 km (1,488 mi) |
| Inclination | 78.6° |
| Period | 115.9 minutes |
| Instruments | |
| Satellite Drag Atmospheric Density | |
Explorer program | |
Explorer 19, (Air Density experiment A, or AD-A), was a NASA satellite launched on 19 December 1963, as part of the Explorer program. It was the third of six identical Explorer satellites launched to study air density and composition, and the second to reach orbit.[1] It was identical to Explorer 9.[2]
- ^ Smith, Woody. "Explorer Spacecraft Series". NASA History Division. Retrieved 10 January 2016.
 This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain.
This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain.
- ^ "AD-A, -B, -C / Explorer S-56, 9, 19, 24, 39". Gunter's Space Page. 8 April 2020. Retrieved 7 November 2021.