| Falx cerebri | |
|---|---|
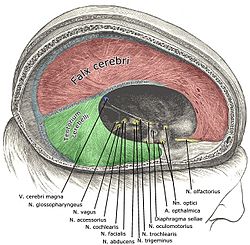 | |
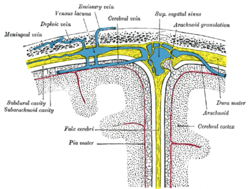 Diagrammatic representation of a section across the top of the skull, showing the membranes of the brain, etc. (Falx cerebri is yellow line running down center.) | |
| Details | |
| Part of | Meninges |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | falx cerebri |
| NeuroNames | 1237 |
| TA98 | A14.1.01.103 |
| TA2 | 5374 |
| FMA | 83967 |
| Anatomical terms of neuroanatomy | |
The falx cerebri (also known as the cerebral falx) is a large, crescent-shaped fold of dura mater that descends vertically into the longitudinal fissure to separate the cerebral hemispheres.[1] It supports the dural sinuses that provide venous and CSF drainage from the brain.[2] It is attached to the crista galli anteriorly, and blends with the tentorium cerebelli posteriorly.[3]
The falx cerebri is often subject to age-related calcification, and a site of falcine meningiomas.[2]
The falx cerebri is named for its sickle-like shape.[4]
- ^ Saladin K. "Anatomy & Physiology: The Unity of Form and Function. New York: McGraw Hill, 2014. Print. pp 512, 770-773
- ^ a b Bair, Michael M.; Munakomi, Sunil (2022), "Neuroanatomy, Falx Cerebri", StatPearls, Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing, PMID 31424888, retrieved 2022-04-26
- ^ Standring, Susan (2020). Gray's Anatomy: The Anatomical Basis of Clinical Practice (42th ed.). New York. p. 398. ISBN 978-0-7020-7707-4. OCLC 1201341621.
{{cite book}}: CS1 maint: location missing publisher (link) - ^ "Falx". Retrieved 10 August 2024.