| Fat-Tailed Dwarf Lemur | |
|---|---|

| |
| Scientific classification | |
| Domain: | Eukaryota |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Chordata |
| Class: | Mammalia |
| Order: | Primates |
| Suborder: | Strepsirrhini |
| Family: | Cheirogaleidae |
| Genus: | Cheirogaleus |
| Species: | C. medius
|
| Binomial name | |
| Cheirogaleus medius É. Geoffroy, 1812[3]
| |
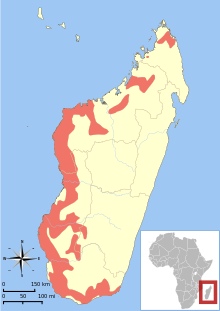
| |
| Fat-tailed dwarf lemur range[1] | |
| Synonyms | |
| |
The fat-tailed dwarf lemur (Cheirogaleus medius), also known as the lesser dwarf lemur, western fat-tailed dwarf lemur, or spiny forest dwarf lemur, is endemic to Madagascar.
The fat-tailed dwarf lemur is 8–9 in (200–230 mm) long from its head to the end of its torso, with an 8–11 in (200–280 mm) tail extending beyond that. It weighs 4–10 oz (110–280 g). It has a lifespan of 4-11 years in the wild and 18 years in captivity. It uses its tail to store fat reserves for torpor.[4]
- ^ a b Blanco, M.; Dolch, R.; Ganzhorn, J.; Greene, L.K.; Le Pors, B.; Lewis, R.; Louis, E.E.; Rafalinirina, H.A.; Raharivololona, B.; Rakotoarisoa, G.; Ralison, J.; Randriahaingo, H.N.T.; Rasoloarison, R.M.; Razafindrasolo, M.; Sgarlata, G.M.; Wright, P.; Zaonarivelo, J. (2020). "Cheirogaleus medius". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2020: e.T163023599A115588562. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2020-2.RLTS.T163023599A115588562.en. Retrieved 19 November 2021.
- ^ Harcourt, C. (1990). Thornback, J (ed.). Lemurs of Madagascar and the Comoros: The IUCN Red Data Book (PDF). World Conservation Union. ISBN 978-2-88032-957-0. OCLC 28425691.
- ^ Groves, C. P. (2005). "Order Primates". In Wilson, D. E.; Reeder, D. M (eds.). Mammal Species of the World: A Taxonomic and Geographic Reference (3rd ed.). Johns Hopkins University Press. p. 112. ISBN 978-0-8018-8221-0. OCLC 62265494.
- ^ "Fat-Tailed Dwarf Lemur, Cheirogaleus medius | New England Primate Conservancy". neprimateconservancy.org. 2021-12-20. Retrieved 2024-05-22.
