| Flocculonodular lobe | |
|---|---|
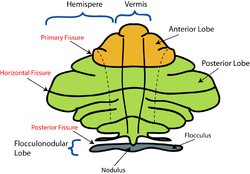 Schematic representation of the major anatomical subdivisions of the cerebellum. Superior view of an "unrolled" cerebellum, placing the vermis in one plane. | |
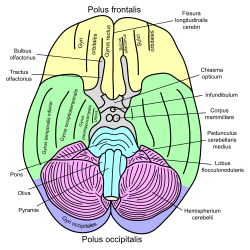 Basal view of a human brain | |
| Identifiers | |
| NeuroNames | 679 |
| NeuroLex ID | birnlex_904 |
| TA98 | A14.1.07.301 |
| TA2 | 5799 |
| FMA | 72253 |
| Anatomical terms of neuroanatomy | |
The flocculonodular lobe (vestibulocerebellum) is one of the lobes of the cerebellum. It is a small lobe consisting of the unpaired midline nodule and the two flocculi: one flocculus on either side of the nodule. The lobe is involved in maintaining posture and balance as well as coordinating head-eye movements.[1]
The lobe is functionally associated with the vestibular system and is therefore also referred to as the vestibulocerebellum. It receives second-order fiber afferents from the vestibular nuclei as well as direct first-order afferents from the vestibular ganglion/nerve (the only region of the cerebellum to do so).[1]
The lobe in turn projects efferents back to the vestibular nuclei which in turn give rise or project to: the lateral vestibulospinal tracts which maintain posture and balance by regulating tone of the axial and proximal limb extensor mucles (i.e. the antigravity muscles); the medial vestibulospinal tracts which regulate the tone of neck muscles; and the medial longitudinal fasciculi which coordinates head-eye movements (vestibuloocular reflex).[1]
- ^ a b c Patestas, Maria A.; Gartner, Leslie P. (2016). A Textbook of Neuroanatomy (2nd ed.). Hoboken, New Jersey: Wiley-Blackwell. pp. 287–288. ISBN 978-1-118-67746-9.