| |||
| Names | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
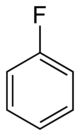
Fluorobenzene | |||
| Other names
Phenyl fluoride
Monofluorobenzene | |||
| Identifiers | |||
3D model (JSmol)
|
|||
| 1236623 | |||
| ChEBI | |||
| ChEMBL | |||
| ChemSpider | |||
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.006.657 | ||
| EC Number |
| ||
| 49856 | |||
| KEGG | |||
PubChem CID
|
|||
| UNII | |||
| UN number | 2387 | ||
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|||
| |||
| |||
| Properties | |||
| C6H5F | |||
| Molar mass | 96.103 | ||
| Appearance | Colorless liquid | ||
| Density | 1.025 g/mL, liquid | ||
| Melting point | −44 °C (−47 °F; 229 K) | ||
| Boiling point | 84 to 85 °C (183 to 185 °F; 357 to 358 K) | ||
| low | |||
| -58.4·10−6 cm3/mol | |||
Refractive index (nD)
|
1.46553 | ||
| Structure | |||
| Planar | |||
| Hazards | |||
| GHS labelling: | |||
  
| |||
| Warning | |||
| H225, H318, H411 | |||
| P210, P233, P240, P241, P242, P243, P264, P273, P280, P303+P361+P353, P305+P351+P338, P310, P337+P313, P370+P378, P391, P403+P235, P501 | |||
| NFPA 704 (fire diamond) | |||
| Related compounds | |||
Related halobenzenes
|
Chlorobenzene Bromobenzene Iodobenzene | ||
Related compounds
|
Benzene 1,2-Difluorobenzene | ||
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |||
Fluorobenzene is an aryl fluoride and the simplest of the fluorobenzenes, with the formula C6H5F, often abbreviated PhF. A colorless liquid, it is a precursor to many fluorophenyl compounds.