 | |
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Pronunciation | Leucovorin /ˌljuːkoʊˈvɔːrɪn/ |
| Trade names | Many |
| Other names | citrovorum factor, 5-formyltetrahydrofolate |
| AHFS/Drugs.com | Monograph |
| MedlinePlus | a608038 |
| License data | |
| Pregnancy category |
|
| Routes of administration | Intravenous, IM, by mouth |
| ATC code | |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status |
|
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Bioavailability | Dose dependent |
| Protein binding | ~15% |
| Elimination half-life | 6.2 hours |
| Excretion | Kidney |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| IUPHAR/BPS | |
| DrugBank | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| ChEMBL | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.000.328 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
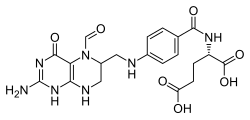
| Formula | C20H23N7O7 |
| Molar mass | 473.446 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| Melting point | 245 °C (473 °F) decomp |
| Solubility in water | ~0.3[1] mg/mL (20 °C) |
| |
| |
| | |
Folinic acid, also known as leucovorin, is a medication used to decrease the toxic effects of methotrexate and pyrimethamine.[2][3] It is also used in combination with 5-fluorouracil to treat colorectal cancer and pancreatic cancer, may be used to treat folate deficiency that results in anemia, and methanol poisoning.[3][4] It is taken by mouth, injection into a muscle, or injection into a vein.[3]
Side effects may include trouble sleeping, allergic reactions, or fever.[2][3] Use in pregnancy or breastfeeding is generally regarded as safe.[2] When used for anemia it is recommended that pernicious anemia as a cause be ruled out first.[3] Folinic acid is a form of folic acid that does not require activation by dihydrofolate reductase to be useful to the body.[3]
Folinic acid was first made in 1945.[5] It is on the World Health Organization's List of Essential Medicines.[6]
- ^ "Safety Data Sheet Folinic Acid (calcium salt)" (PDF). Retrieved 25 January 2018.
- ^ a b c British national formulary : BNF 69 (69 ed.). British Medical Association. 2015. pp. 576–577. ISBN 9780857111562.
- ^ a b c d e f "Leucovorin Calcium". The American Society of Health-System Pharmacists. Archived from the original on 10 May 2017. Retrieved 8 December 2016.
- ^ Munjal YP, Sharm SK (2012). API Textbook of Medicine, Ninth Edition, Two Volume Set. JP Medical Ltd. p. 1945. ISBN 9789350250747. Archived from the original on 10 May 2017.
- ^ Sneader W (2005). Drug Discovery: A History. John Wiley & Sons. p. 235. ISBN 9780471899792. Archived from the original on 10 May 2017.
- ^ World Health Organization (2019). World Health Organization model list of essential medicines: 21st list 2019. Geneva: World Health Organization. hdl:10665/325771. WHO/MVP/EMP/IAU/2019.06. License: CC BY-NC-SA 3.0 IGO.