 | |
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Trade names | Rukobia |
| Other names | BMS-663068, GSK3684934 |
| AHFS/Drugs.com | Monograph |
| MedlinePlus | a620046 |
| License data |
|
| Pregnancy category |
|
| Routes of administration | By mouth |
| ATC code | |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status | |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| DrugBank | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
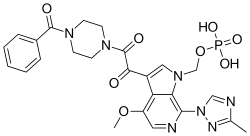
| Formula | C25H26N7O8P |
| Molar mass | 583.498 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
Fostemsavir, sold under the brand name Rukobia, is an antiretroviral medication for adults living with HIV/AIDS who have tried multiple HIV medications and whose HIV infection cannot be successfully treated with other therapies because of resistance, intolerance or safety considerations.[4][7]
The most common adverse reaction is nausea.[4][7][8] Severe adverse reactions included elevations in liver enzymes among participants also infected with hepatitis B or C virus, and changes in the immune system (immune reconstitution syndrome).[7]
Fostemsavir is an HIV entry inhibitor and a prodrug of temsavir (BMS-626529).[9] Fostemsavir is a human immunodeficiency virus type 1 (HIV-1) gp120-directed attachment inhibitor.[10]
It was approved for medical use in the United States in July 2020,[7][8][10] and in the European Union in February 2021.[5] The U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) considers it to be a first-in-class medication.[11]
- ^ a b "Rukobia". Therapeutic Goods Administration (TGA). 23 July 2021. Retrieved 5 September 2021.
- ^ "Notice: Multiple Additions to the Prescription Drug List (PDL) [2022-01-24]". Health Canada. 24 January 2022. Retrieved 28 May 2022.
- ^ "Summary Basis of Decision (SBD) for Rukobia". Health Canada. 23 October 2014. Retrieved 29 May 2022.
- ^ a b c "Rukobia- fostemsavir tromethamine tablet, film coated, extended release". DailyMed. 2 July 2020. Retrieved 14 July 2020.
- ^ a b "Rukobia EPAR". European Medicines Agency (EMA). 9 December 2020. Retrieved 12 February 2021.
- ^ "Rukobia Product information". Union Register of medicinal products. Retrieved 3 March 2023.
- ^ a b c d "FDA Approves New HIV Treatment for Patients With Limited Treatment Options". U.S. Food and Drug Administration (Press release). 2 July 2020. Retrieved 2 July 2020.
 This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain.
This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain.
- ^ a b Cite error: The named reference
FDA snapshotwas invoked but never defined (see the help page). - ^ Lai YT, Wang T, O'Dell S, Louder MK, Schön A, Cheung CS, et al. (January 2019). "Lattice engineering enables definition of molecular features allowing for potent small-molecule inhibition of HIV-1 entry". Nature Communications. 10 (1): 47. Bibcode:2019NatCo..10...47L. doi:10.1038/s41467-018-07851-1. PMC 6318274. PMID 30604750.
- ^ a b Cite error: The named reference
ViiV PRwas invoked but never defined (see the help page). - ^ "New Drug Therapy Approvals 2020". U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA). 31 December 2020. Retrieved 17 January 2021.
 This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain.
This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain.