| Fraser River | |
|---|---|
 The Fraser River, from the grounds of Westminster Abbey, above Hatzic in Mission, British Columbia, looking upstream (E) | |
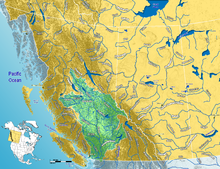 Fraser River watershed | |
| Etymology | Fur trader and explorer Simon Fraser |
| Location | |
| Country | Canada |
| Province | British Columbia |
| Regional districts | |
| Cities |
|
| Physical characteristics | |
| Source | Fraser Pass |
| • location | Mount Robson Provincial Park, Rocky Mountains, British Columbia, Canada |
| • coordinates | 52°37′41″N 118°25′50″W / 52.62806°N 118.43056°W |
| • elevation | 2,145 m (7,037 ft) |
| Mouth | Fraser River Delta |
• location | Strait of Georgia, Vancouver, British Columbia, Canada |
• coordinates | 49°10′40″N 123°12′45″W / 49.17778°N 123.21250°W |
• elevation | 0 m (0 ft) |
| Length | 1,375 km (854 mi)[5] |
| Basin size | 220,000 km2 (85,000 sq mi) |
| Discharge | |
| • location | mouth (average and min); max at Hope[6][7] |
| • average | 3,475 m3/s (122,700 cu ft/s) |
| • minimum | 575 m3/s (20,300 cu ft/s) |
| • maximum | 17,000 m3/s (600,000 cu ft/s) |
| Basin features | |
| Tributaries | |
| • left | Bowron River, Willow River, Quesnel River, Thompson River, Coquihalla River, Chilliwack River, Sumas River, Salmon River (lower mainland) |
| • right | Morkill River, McGregor River, Salmon River (interior), Nechako River, West Road (Blackwater) River, Chilcotin River, Bridge River, Harrison River, Stave River, Pitt River, Coquitlam River |
| Protection status | |
| Official name | Fraser River Delta |
| Designated | 24 May 1982 |
| Reference no. | 243[8] |
The Fraser River (/ˈfreɪzər/) is the longest river within British Columbia, Canada, rising at Fraser Pass near Blackrock Mountain in the Rocky Mountains and flowing for 1,375 kilometres (854 mi), into the Strait of Georgia just south of the City of Vancouver.[5][9] The river's annual discharge at its mouth is 112 cubic kilometres (27 cu mi) or 3,550 cubic metres per second (125,000 cu ft/s), and each year it discharges about 20 million tons of sediment into the ocean.[10]
- ^ Salishan languages and Chinook Jargon. The Halkomelem form is Sto:lo, used as the name of the people of the Fraser Valley stretch of the river. "Staulo" is the anglicization used in the Kamloops Wawa lexicon of the Chinook Jargon
- ^ Carrier language. Lhtako is also used to mean the Dakelh people of the Quesnel/North Cariboo area
- ^ Indigenous name recorded by Alexander Mackenzie on expedition to find Columbia River’s headwaters; circa 18-?
- ^ Tsilhqot'in name meaning Sturgeon (ʔElhdachogh) River (Yeqox)
- ^ a b "Fraser River Fact Sheet". Canadian Heritage Rivers System. Archived from the original on July 12, 2017. Retrieved December 2, 2016.
- ^ Ambient Water Quality Assessment and Objectives for the Fraser River sub-basin from Kanaka Creek to the Mouth Archived March 4, 2016, at the Wayback Machine, BC Ministry of Environment
- ^ Cite error: The named reference
reviewwas invoked but never defined (see the help page). - ^ "Fraser River Delta". Ramsar Sites Information Service. Retrieved April 25, 2018.
- ^ "BC Geographical Names". Retrieved June 2, 2019.
- ^ Cannings, Richard and Sidney. British Columbia: A Natural History. p.41. Greystone Books. Vancouver. 1996
