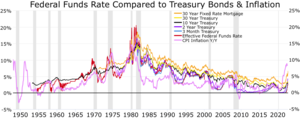
The Friedman rule is a monetary policy rule proposed by Milton Friedman.[1] Friedman advocated monetary policy that would result in the nominal interest rate being at or very near zero. His rationale was that the opportunity cost of holding money faced by private agents should equal the social cost of creating additional fiat money. Assuming that the marginal cost of creating additional money is zero (or approximated by zero), nominal rates of interest should also be zero. In practice, this means that a central bank should seek a rate of inflation or deflation equal to the real interest rate on government bonds and other safe assets, to make the nominal interest rate zero.
The result of this policy is that those who hold money do not suffer any loss in the value of that money due to inflation. The rule is motivated by long-run efficiency considerations.
This is not to be confused with Friedman's k-percent rule which advocates a constant yearly expansion of the monetary base.
- ^ M. Friedman (1969), The Optimum Quantity of Money, Macmillan