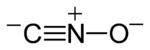
| |
| Identifiers | |
|---|---|
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChEBI | |
| ChemSpider | |
| 239442 | |
PubChem CID
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| CNO− | |
| Molar mass | 42.018 g·mol−1 |
| Conjugate acid | Fulminic acid |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
Fulminates are chemical compounds which include the fulminate ion (CNO−, C−≡N+−O−). The fulminate ion is a pseudohalic ion because its charge and reactivity are similar to those of the halogens. Due to the instability of the ion, fulminate salts are friction-sensitive explosives. The best known is mercury(II) fulminate, which has been used as a primary explosive in detonators. Fulminates can be formed from metals, such as silver and mercury, dissolved in nitric acid and reacted with ethanol. The weak single nitrogen-oxygen bond is responsible for their instability. Nitrogen very easily forms a stable triple bond to another nitrogen atom, forming nitrogen gas.