 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Pronunciation | /fʊlˈvɛstrənt/ fuul-VES-trənt |
| Trade names | Faslodex, others |
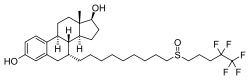
| Other names | ICI-182780; ZD-182780; ZD-9238; 7α-[9-[(4,4,5,5,5-Pentafluoropentyl)-sulfinyl]nonyl]estra-1,3,5(10)-triene-3,17β-diol |
| AHFS/Drugs.com | Monograph |
| MedlinePlus | a607031 |
| License data |
|
| Pregnancy category |
|
| Routes of administration | Intramuscular injection |
| Drug class | Antiestrogen |
| ATC code | |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status | |
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Bioavailability | Low[4] |
| Protein binding | 99%[4] |
| Metabolism | Hydroxylation, conjugation (glucuronidation, sulfation)[4] |
| Elimination half-life | IM: 40–50 days[4] |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| IUPHAR/BPS | |
| DrugBank | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.170.955 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C32H47F5O3S |
| Molar mass | 606.78 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
| | |
Fulvestrant, sold under the brand name Faslodex among others, is an antiestrogenic medication used to treat hormone receptor (HR)-positive metastatic breast cancer in postmenopausal women with disease progression as well as HR-positive, HER2-negative advanced breast cancer in combination with abemaciclib or palbociclib in women with disease progression after endocrine therapy.[2] It is given by injection into a muscle.[5]
Fulvestrant is a selective estrogen receptor degrader (SERD) and was first-in-class to be approved.[6] It works by binding to the estrogen receptor and destabilizing it, causing the cell's normal protein degradation processes to destroy it.[6]
Fulvestrant was approved for medical use in the United States in 2002.[7]
- ^ Cite error: The named reference
UKlabel2016was invoked but never defined (see the help page). - ^ a b "Faslodex- fulvestrant injection". DailyMed. 25 September 2020. Archived from the original on 11 December 2023. Retrieved 24 May 2024.
- ^ "Faslodex". European Medicines Agency (EMA). 10 March 2004. Archived from the original on 19 October 2021. Retrieved 24 May 2024.
- ^ a b c d Dörwald FZ (4 February 2013). Lead Optimization for Medicinal Chemists: Pharmacokinetic Properties of Functional Groups and Organic Compounds. John Wiley & Sons. pp. 486–. ISBN 978-3-527-64565-7. Archived from the original on 12 January 2023. Retrieved 20 May 2018.
- ^ Lee CI, Goodwin A, Wilcken N (January 2017). "Fulvestrant for hormone-sensitive metastatic breast cancer". The Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews. 1 (1): CD011093. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD011093.pub2. PMC 6464820. PMID 28043088.
- ^ a b Lai AC, Crews CM (February 2017). "Induced protein degradation: an emerging drug discovery paradigm". Nature Reviews. Drug Discovery. 16 (2): 101–114. doi:10.1038/nrd.2016.211. PMC 5684876. PMID 27885283.
- ^ "Fulvestrant". The American Society of Health-System Pharmacists. Archived from the original on 2 February 2017. Retrieved 8 January 2017.