| |

| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Other names
Gallium trichloride, Trichlorogallium, Trichlorogallane
| |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.033.268 |
PubChem CID
|
|
| RTECS number |
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|
| |
| Properties | |
| GaCl 3 | |
| Molar mass | 176.073 g/mol (anhydrous) 194.10 g/mol (monohydrate) |
| Appearance | colorless crystals |
| Density | 2.47 g/cm3 (anhydrous) |
| Melting point | 77.9 °C (172.2 °F; 351.0 K) (anhydrous) 44.4 °C (monohydrate) |
| Boiling point | 201 °C (394 °F; 474 K) (anhydrous) |
| very soluble | |
| Solubility | soluble in benzene, CCl4, CS2, and alkanes |
| −63.0·10−6 cm3/mol | |
| Structure[1] | |
| monoclinic | |
| C2/m | |
a = 11.95 Å, b = 6.86 Å, c = 7.05 Å α = 90°, β = 125.7°, γ = 90°
| |
Lattice volume (V)
|
469 Å3 |
| Hazards | |
| GHS labelling: | |

| |
| Danger | |
| H314 | |
| NFPA 704 (fire diamond) | |
| Flash point | Non-flammable |
| Lethal dose or concentration (LD, LC): | |
LD50 (median dose)
|
4700 mg/kg (rat, oral) |
| Related compounds | |
Other anions
|
Gallium(III) fluoride Gallium(III) bromide Gallium(III) iodide |
Other cations
|
Aluminium chloride Indium(III) chloride Thallium(III) chloride |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
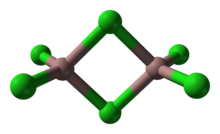
Gallium(III) chloride is an inorganic chemical compound with the formula GaCl3 which forms a monohydrate, GaCl3·H2O. Solid gallium(III) chloride is a deliquescent white solid and exists as a dimer with the formula Ga2Cl6.[2] It is colourless and soluble in virtually all solvents, even alkanes, which is truly unusual for a metal halide. It is the main precursor to most derivatives of gallium and a reagent in organic synthesis.[3]
As a Lewis acid, GaCl3 is milder than aluminium chloride. It is also easier to reduce than aluminium chloride. The coordination chemistry of Ga(III) and Fe(III) are similar, so gallium(III) chloride has been used as a diamagnetic analogue of ferric chloride.
- ^ Cite error: The named reference
strwas invoked but never defined (see the help page). - ^ Wells, A.F. (1984) Structural Inorganic Chemistry, Oxford: Clarendon Press. ISBN 0-19-855370-6.
- ^ Yamaguchi, Masahiko; Matsunaga, Shigeki; Shibasaki, Masakatsu; Michelet, Bastien; Bour, Christophe; Gandon, Vincent (2014), "Gallium Trichloride", Encyclopedia of Reagents for Organic Synthesis, John Wiley & Sons, Ltd, pp. 1–8, doi:10.1002/047084289x.rn00118u.pub3, ISBN 9780470842898
