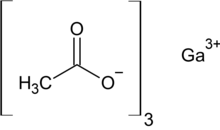
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC names
Tetra-μ2-acetatodiaquadigallium(III), diacetyloxygallanyl acetate
gallium(3+) triacetate
| |
Other names
| |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.018.106 |
| EC Number |
|
PubChem CID
|
|
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| Ga(O2C2H3)3 | |
| Molar mass | 246.85[1] |
| Appearance | white crystals |
| Density | 1.57 g/cm/3 |
| Melting point | N/A |
| Boiling point | 117.1C |
| Hazards | |
| GHS labelling: | |
 
| |
| Danger | |
| H314, H335 | |
| P261, P280, P304+P340, P305+P351+P338, P405, P501 | |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |

Gallium acetate is a salt composed of a gallium atom trication and three acetate groups as anions where gallium exhibits the +3 oxidation state. It has a chemical formula of Ga(CH3COO)3 although it can be informally referred to as GaAc because Ac is an informal symbol for acetate. Gallium is moderately water-soluble and decomposes to gallium oxide when heated to around 70 °C.[2] Gallium acetate, like other acetate compounds, is a good precursor to ultra-pure compounds, catalysts and nanoscale materials.[2] Gallium acetate is being considered as a substitute in de-icing compounds like calcium chloride and magnesium chloride.[3]
- ^ "Gallium acetate".
- ^ a b Elements, American. "Gallium Acetate". American Elements. Retrieved 2022-05-05.
- ^ "Gallium acetate, 99.9% 2571-06-4 - Manufacturers & Suppliers in India with worldwide shipping". www.ottokemi.com. Retrieved 2022-05-05.