 | |
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Pronunciation | /ɡɛˈfɪtɪnɪb/ |
| Trade names | Iressa, others |
| Other names | ZD1839 |
| AHFS/Drugs.com | Monograph |
| MedlinePlus | a607002 |
| License data | |
| Pregnancy category |
|
| Routes of administration | By mouth |
| ATC code | |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status | |
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Bioavailability | 59% (oral) |
| Protein binding | 90% |
| Metabolism | Liver (mainly CYP3A4) |
| Elimination half-life | 6–49 hours |
| Excretion | Feces |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| IUPHAR/BPS | |
| DrugBank | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.171.043 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
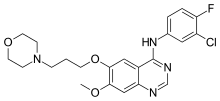
| Formula | C22H24ClFN4O3 |
| Molar mass | 446.91 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
| (verify) | |
Gefitinib, sold under the brand name Iressa, is a medication used for certain breast, lung and other cancers. Gefitinib is an EGFR inhibitor, like erlotinib, which interrupts signaling through the epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) in target cells. Therefore, it is only effective in cancers with mutated and overactive EGFR, but resistances to gefitinib can arise through other mutations. It is marketed by AstraZeneca and Teva.
It is on the World Health Organization's List of Essential Medicines.[5] It is available as a generic medication.[6]
- ^ https://www.tga.gov.au/resources/auspar/auspar-gefitinib [bare URL]
- ^ "Iressa Product information". Health Canada. 17 December 2003. Retrieved 31 March 2024.
- ^ "Iressa- gefitinib tablet, coated". DailyMed. 28 February 2023. Retrieved 31 March 2024.
- ^ "Iressa EPAR". European Medicines Agency (EMA). 24 June 2009. Retrieved 31 March 2024.
- ^ World Health Organization (2023). The selection and use of essential medicines 2023: web annex A: World Health Organization model list of essential medicines: 23rd list (2023). Geneva: World Health Organization. hdl:10665/371090. WHO/MHP/HPS/EML/2023.02.
- ^ "First Generic Drug Approvals". U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA). 17 October 2022. Retrieved 28 November 2022.