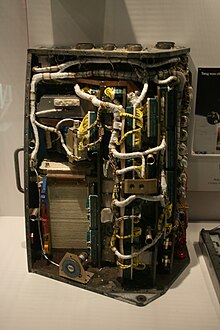
 Gemini Guidance Computer in National Air and Space Museum | |
| Invented by | IBM Federal Systems Division |
|---|---|
| Manufacturer | IBM Federal Systems Division |
| Introduced | 1965 |
| Discontinued | 1966 |
| Type | Avionics Guidance Computer |
| Processor | Discrete Components [1] |
| Frequency | 7.143 kilohertz clock |
| Memory | 39-bit words memory, each composed of three 13-bit syllables, 4,096 words of memory, in a ferrite core array. |
| Ports | Modular Display Keyboard (MDK), Modular Display Readout (MDR), Attitude Control and Maneuver Electronics (ACME), Inertial Measurement Unit (IMU), Horizon Sensors, Time Reference System (TRS)[2] |
| Weight | 58.98 lb (26.75 kg) |
| Dimensions | 18.9 in × 14.5 in × 12.75 in (48.0 cm × 36.8 cm × 32.4 cm) (H)×(W)×(D) |
The Gemini Guidance Computer (sometimes Gemini Spacecraft On-Board Computer (OBC)) was a digital, serial computer designed for Project Gemini, America's second human spaceflight project.[3] The computer, which facilitated the control of mission maneuvers, was designed by the IBM Federal Systems Division.[4]
- ^ Tomayko, James E. (March 1988). "Ch1-2".
- ^ "The Gemini Spacecraft Computer".
- ^ Cite error: The named reference
manualwas invoked but never defined (see the help page). - ^ 8. J. C. Hundley and R. A. Watson, "A Digital Computer in Orbital Flight," TR 63-825-892, IBM Federal Systems Division, Owego, New York, October 1964.