  | |
| Continent | Africa |
|---|---|
| Region | West Africa Sub-Saharan Africa |
| Coordinates | 9°30′N 2°15′E / 9.500°N 2.250°E |
| Area | Ranked 102nd |
| • Total | 112,622 km2 (43,484 sq mi) |
| • Land | 98.2% |
| • Water | 1.8% |
| Coastline | 121 km (75 mi) |
| Borders | Total land borders: 2,123 km (1,319 mi) Burkina Faso 386 km (240 mi), Niger 277 km (172 mi), Nigeria 809 km (503 mi), Togo 651 km (405 mi) |
| Highest point | Mont Sokbaro 658 m (2,159 ft) |
| Lowest point | Atlantic Ocean sea level |
| Terrain | flat to undulating plain; some hills and mountains |
| Natural resources | oil, limestone, marble, timber |
| Environmental issues | deforestation, desertification |
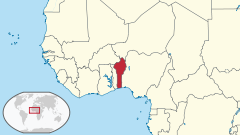
Benin, a narrow, key-shaped, north–south strip of land in West Africa, lies between the Equator and the Tropic of Cancer. Its latitude ranges from 6°30′ N to 12°30′ N and its longitude from 1° E to 3°40′ E. It is bounded by Togo to the west, Burkina Faso and Niger to the north, Nigeria to the east, and the Bight of Benin to the south.
With an area of 112,622 km2 (43,484 sq mi), it is slightly bigger than the nation of Bulgaria. It extends from the Niger River in the north to the Atlantic Ocean in the south, a distance of 700 km (435 mi). Although the coastline measures 121 km (75 mi), the country measures about 325 km (202 mi) at its widest point.
It is one of the smaller countries in West Africa, about one eighth the size of Nigeria, its neighbor to the east. It is, however, twice as large as Togo, its neighbor to the west. A relief map of Benin shows that it has little variation in elevation, averaging 200 m (656 ft) in elevation.