 | |
| Continent | Eurasia |
|---|---|
| Region | Eastern Mediterranean |
| Coordinates | 33°50′N 35°50′E / 33.833°N 35.833°E |
| Area | Ranked 161st |
| • Total | 10,452 km2 (4,036 sq mi) |
| • Land | 98.37% |
| • Water | 1.63% |
| Coastline | 225 km (140 mi) |
| Highest point | Qurnat as Sawda' 3,088 m (10,131 ft) |
| Lowest point | Mediterranean Sea 0 m (0 ft) |
| Longest river | Litani River 140 km (87 mi) |
| Largest lake | Lake Qaraoun 1,600 km2 (620 sq mi) |
| Climate | Mediterranean |
| Natural resources | Limestone, iron ore, salt, water-surplus state in a water-deficit region, arable land |
| Natural hazards | dust storms |
| Environmental issues | deforestation, soil erosion, desertification, air pollution |
| Exclusive economic zone | 19,516 km2 (7,535 sq mi) |
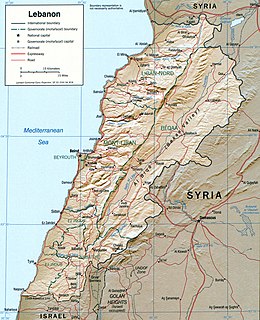
Lebanon is a small country in the Levant region of the Eastern Mediterranean, located at approximately 34˚N, 35˚E. It stretches along the eastern shore of the Mediterranean Sea and its length is almost three times its width. From north to south, the width of its terrain becomes narrower. Lebanon's mountainous terrain, proximity to the sea, and strategic location at a crossroads of the world were decisive factors in shaping its history.[1]
The country's role in the region, as indeed in the world at large, was shaped by trade.[1] It serves as a link between the Mediterranean world and India and East Asia.[1] The merchants of the region exported oil, grain, textiles, metal work, and pottery through the port cities to Western markets.[1]
- ^ a b c d
 This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain: AbuKhalil, As'ad (1989). "Geography". In Collelo, Thomas (ed.). Lebanon: a country study. Washington, D.C.: Federal Research Division, Library of Congress. pp. 42–48. OCLC 44356055.
This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain: AbuKhalil, As'ad (1989). "Geography". In Collelo, Thomas (ed.). Lebanon: a country study. Washington, D.C.: Federal Research Division, Library of Congress. pp. 42–48. OCLC 44356055.