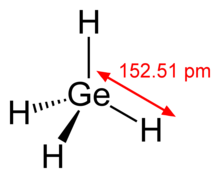
| |||
| |||
| Names | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| IUPAC name
Germane
| |||
| Other names
Germanium tetrahydride
Germanomethane Monogermane | |||
| Identifiers | |||
3D model (JSmol)
|
|||
| ChEBI | |||
| ChemSpider | |||
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.029.055 | ||
| EC Number |
| ||
| 587 | |||
| KEGG | |||
PubChem CID
|
|||
| RTECS number |
| ||
| UNII | |||
| UN number | 2192 | ||
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|||
| |||
| |||
| Properties | |||
| GeH4 | |||
| Molar mass | 76.62 g/mol | ||
| Appearance | Colorless gas | ||
| Odor | Pungent[1] | ||
| Density | 3.3 kg/m3 | ||
| Melting point | −165 °C (−265 °F; 108 K) | ||
| Boiling point | −88 °C (−126 °F; 185 K) | ||
| Low | |||
| Vapor pressure | >1 atm[1] | ||
| Viscosity | 17.21 μPa·s (theoretical estimate)[2] | ||
| Structure | |||
| Tetrahedral | |||
| 0 D | |||
| Hazards | |||
| Occupational safety and health (OHS/OSH): | |||
Main hazards
|
Toxic, flammable, may ignite spontaneously in air | ||
| GHS labelling: | |||
  
| |||
| Danger | |||
| H220, H302, H330 | |||
| P210, P260, P264, P270, P271, P284, P301+P312, P304+P340, P310, P320, P330, P377, P381, P403, P403+P233, P405, P410+P403, P501 | |||
| NFPA 704 (fire diamond) | |||
| NIOSH (US health exposure limits): | |||
PEL (Permissible)
|
None[1] | ||
REL (Recommended)
|
TWA 0.2 ppm (0.6 mg/m3)[1] | ||
IDLH (Immediate danger)
|
N.D.[1] | ||
| Safety data sheet (SDS) | ICSC 1244 | ||
| Related compounds | |||
Related compounds
|
Methane Silane Stannane Plumbane Germyl | ||
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |||
Germane is the chemical compound with the formula GeH4, and the germanium analogue of methane. It is the simplest germanium hydride and one of the most useful compounds of germanium. Like the related compounds silane and methane, germane is tetrahedral. It burns in air to produce GeO2 and water. Germane is a group 14 hydride.
- ^ a b c d e NIOSH Pocket Guide to Chemical Hazards. "#0300". National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health (NIOSH).
- ^ Yaws, Carl L. (1997), Handbook Of Viscosity: Volume 4: Inorganic Compounds And Elements, Gulf Professional Publishing, ISBN 978-0123958501


